TP-Link TL-SG2424P TL-SG2424P V1 User Guide 1910010774 - Page 60
DHCP-ACK Stage, DHCP Cheating Attack, Switching, DHCP Filtering - user manual
 |
View all TP-Link TL-SG2424P manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 60 highlights
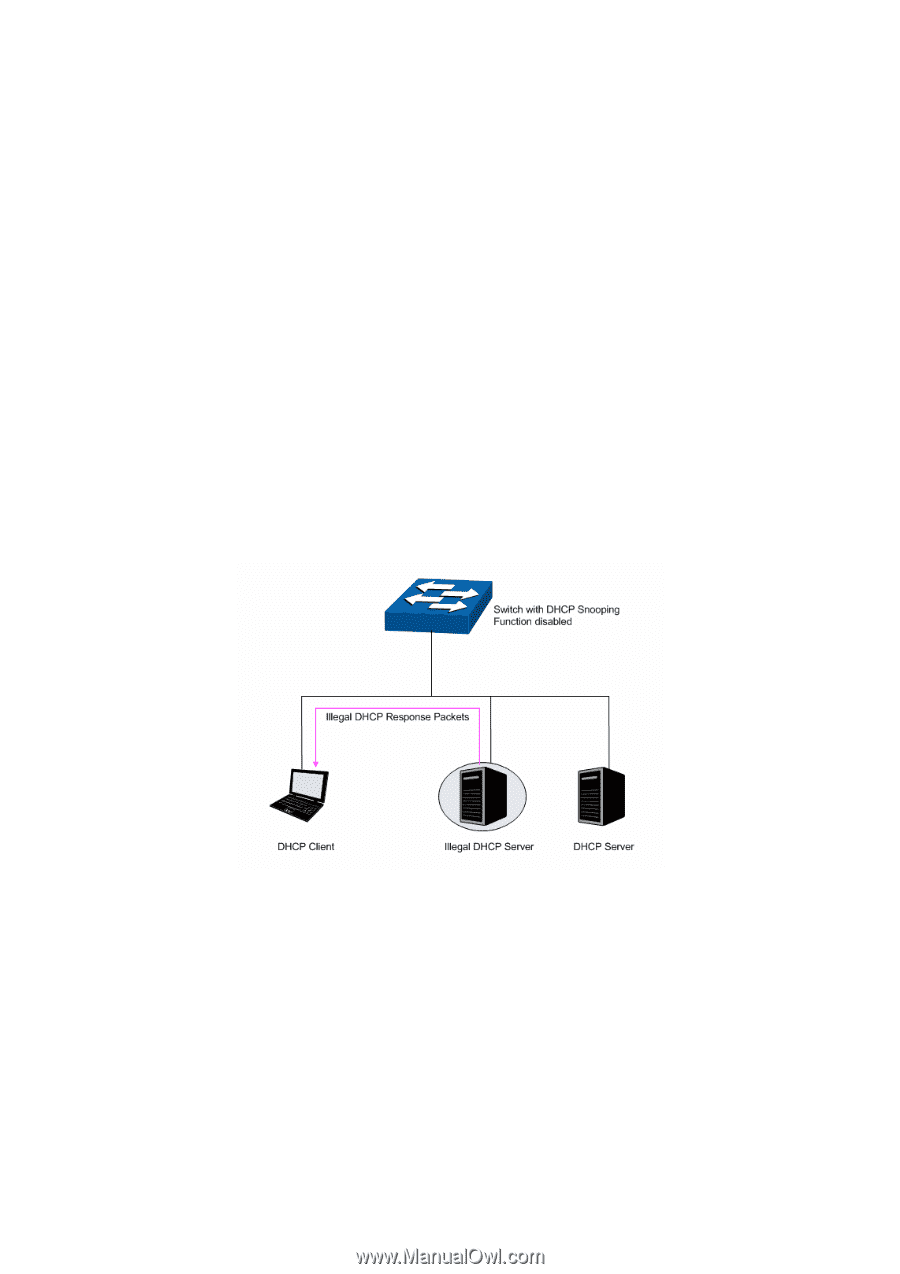
packet and broadcast the DHCP-REQUEST packet which includes the assigned IP address of the DHCP-OFFER packet. (4) DHCP-ACK Stage: Since the DHCP-REQUEST packet is broadcasted, all DHCP servers on the network segment can receive it. However, only the requested server processes the request. If the DHCP server acknowledges assigning this IP address to the client, it will send the DHCP-ACK packet back to the client. Otherwise, the Server will send the DHCP-NAK packet to refuse assigning this IP address to the client. DHCP Cheating Attack During the working process of DHCP, generally there is no authentication mechanism between Server and Client. If there are several DHCP servers in the network, network confusion and security problem will happen. The common cases incurring the illegal DHCP servers are the following two: (1) It's common that the illegal DHCP server is manually configured by the user by mistake. (2) Hacker exhausted the IP addresses of the normal DHCP server and then pretended to be a legal DHCP server to assign the IP addresses and the other parameters to Clients. For example, hacker used the pretended DHCP server to assign a modified DNS server address to users so as to induce the users to the evil financial website or electronic trading website and cheat the users of their accounts and passwords. The following figure illustrates the DHCP Cheating Attack implementation procedure. Figure 5-18 DHCP Cheating Attack Implementation Procedure DHCP Filtering feature allows only the trusted ports to forward DHCP packets and thereby ensures that users get proper IP addresses. DHCP Filtering is to monitor the process of hosts obtaining the IP addresses from DHCP servers, and record the IP address, MAC address, VLAN and the connected Port number of the Host for automatic binding. DHCP Filtering feature prevents the network from the DHCP Server Cheating Attack by discarding the DHCP packets on the distrusted port, so as to enhance the network security. Choose the menu Switching → DHCP Filtering to load the following page. 52