TP-Link TL-SG2424P TL-SG2424P V1 User Guide 1910010774 - Page 84
STP Security
 |
View all TP-Link TL-SG2424P manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 84 highlights
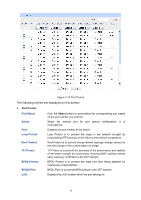
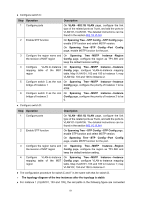
Note: The port status of one port in different spanning tree instances can be different. Global configuration Procedure for Spanning Tree function: Step Operation Description 1 Make clear roles the switches Preparation. play in spanning tree instances: root bridge or designated bridge 2 Globally configure MSTP Required. Enable Spanning Tree function on the switch parameters and configure MSTP parameters on Spanning Tree→STP Config→STP Config page. 3 Configure MSTP parameters Required. Configure MSTP parameters for ports on for ports Spanning Tree→Port Config→Port Config page. 4 Configure the MST region Required. Create MST region and configure the role the switch plays in the MST region on Spanning Tree→MSTP Instance→Region Config and Instance Config page. 5 Configure MSTP parameters Optional. Configure different instances in the MST for instance ports region and configure MSTP parameters for instance ports on Spanning Tree→MSTP Instance→Instance Port Config page. 7.4 STP Security Configuring protection function for devices can prevent devices from any malicious attack against STP features. The STP Security function can be implemented on Port Protect and TC Protect pages. Port Protect function is to prevent the devices from any malicious attack against STP features. 7.4.1 Port Protect On this page you can configure loop protect feature, root protect feature, TC protect feature, BPDU protect feature and BPDU filter feature for ports. You are suggested to enable corresponding protection feature for the qualified ports. Loop Protect In a stable network, a switch maintains the states of ports by receiving and processing BPDU packets from the upstream switch. However, when link congestions or link failures occurred to the network, a down stream switch does not receive BPDU packets for certain period, which results in spanning trees being regenerated and roles of ports being reselected, and causes the blocked ports to transit to forwarding state. Therefore, loops may be incurred in the network. The loop protect function can suppresses loops. With this function enabled, a port, regardless of the role it plays in instances, is always set to blocking state, when the port does not receive BPDU packets from the upstream switch and spanning trees are regenerated, and thereby loops can be prevented. 76