TP-Link TL-SG2424P TL-SG2424P V1 User Guide 1910010774 - Page 64
GENERAL, VLAN Config, Port Config
 |
View all TP-Link TL-SG2424P manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 64 highlights
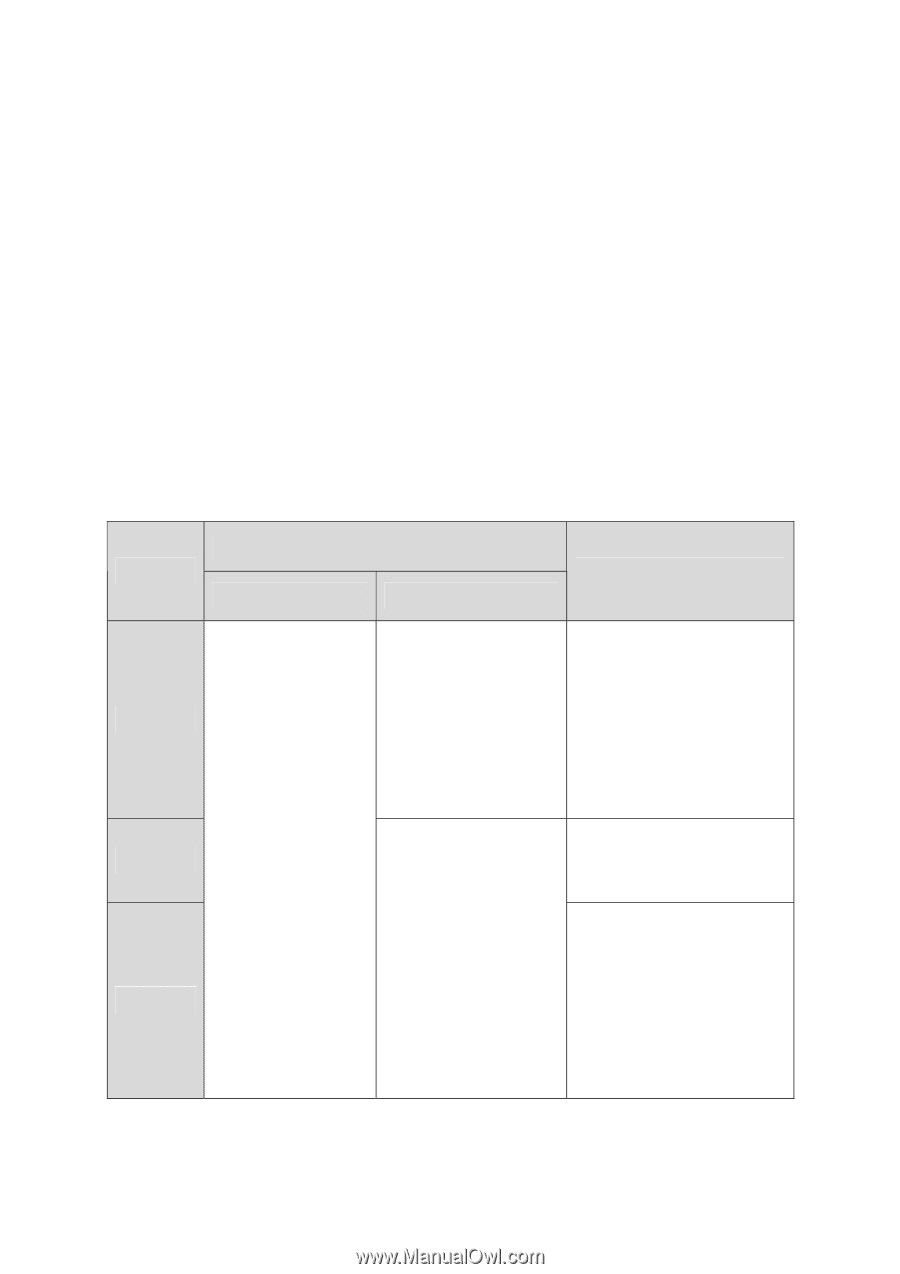
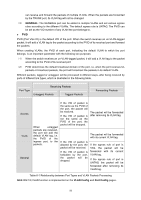
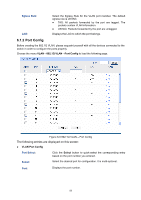
can receive and forward the packets of multiple VLANs. When the packets are forwarded by the TRUNK port, its VLAN tag will not be changed. (3) GENERAL: The GENERAL port can be added in multiple VLANs and set various egress rules according to the different VLANs. The default egress rule is UNTAG. The PVID can be set as the VID number of any VLAN the port belongs to. PVID PVID (Port Vlan ID) is the default VID of the port. When the switch receives an un-VLAN-tagged packet, it will add a VLAN tag to the packet according to the PVID of its received port and forward the packets. When creating VLANs, the PVID of each port, indicating the default VLAN to which the port belongs, is an important parameter with the following two purposes: (1) When the switch receives an un-VLAN-tagged packet, it will add a VLAN tag to the packet according to the PVID of its received port (2) PVID determines the default broadcast domain of the port, i.e. when the port receives UL packets or broadcast packets, the port will broadcast the packets in its default VLAN. Different packets, tagged or untagged, will be processed in different ways, after being received by ports of different link types, which is illustrated in the following table. Port Type Receiving Packets Untagged Packets Tagged Packets Forwarding Packets Access Trunk General When untagged packets are received, the port will add the default VLAN tag, i.e. the PVID of the ingress port, to the packets. If the VID of packet is the same as the PVID of the port, the packet will be received. If the VID of packet is not the same as the PVID of the port, the packet will be dropped. If the VID of packet is allowed by the port, the packet will be received. If the VID of packet is forbidden by the port, the packet will be dropped. The packet will be forwarded after removing its VLAN tag. The packet will be forwarded with its current VLAN tag. If the egress rule of port is TAG, the packet will be forwarded with its current VLAN tag. If the egress rule of port is UNTAG, the packet will be forwarded after removing its VLAN tag. Table 6-1 Relationship between Port Types and VLAN Packets Processing IEEE 802.1Q VLAN function is implemented on the VLAN Config and Port Config pages. 56