ZyXEL P-660H-T1 v2 User Guide - Page 113
Denial of Service
 |
View all ZyXEL P-660H-T1 v2 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 113 highlights
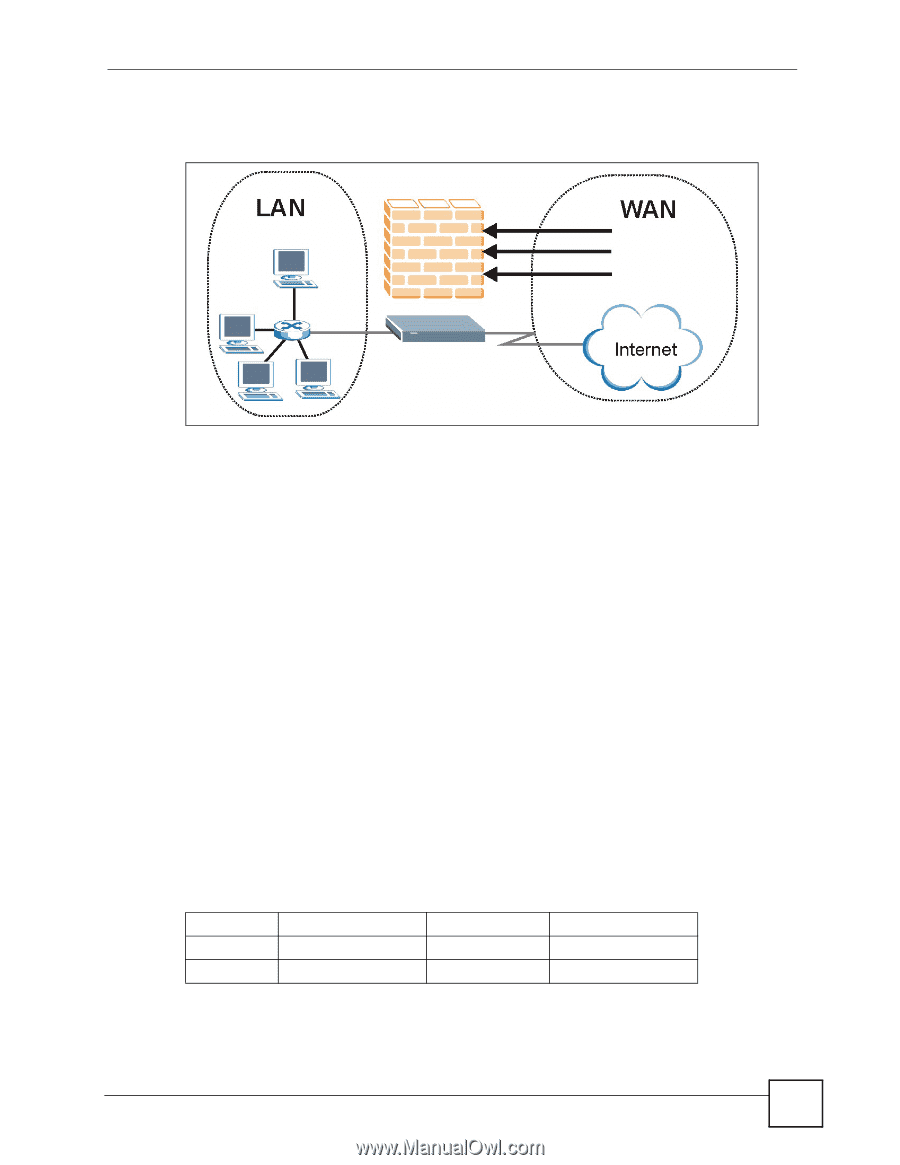
8.3.1 Denial of Service Attacks Figure 58 Firewall Application Chapter 8 Firewalls 8.4 Denial of Service Denials of Service (DoS) attacks are aimed at devices and networks with a connection to the Internet. Their goal is not to steal information, but to disable a device or network so users no longer have access to network resources. The ZyXEL Device is pre-configured to automatically detect and thwart all known DoS attacks. 8.4.1 Basics Computers share information over the Internet using a common language called TCP/IP. TCP/ IP, in turn, is a set of application protocols that perform specific functions. An "extension number", called the "TCP port" or "UDP port" identifies these protocols, such as HTTP (Web), FTP (File Transfer Protocol), POP3 (E-mail), etc. For example, Web traffic by default uses TCP port 80. When computers communicate on the Internet, they are using the client/server model, where the server "listens" on a specific TCP/UDP port for information requests from remote client computers on the network. For example, a Web server typically listens on port 80. Please note that while a computer may be intended for use over a single port, such as Web on port 80, other ports are also active. If the person configuring or managing the computer is not careful, a hacker could attack it over an unprotected port. Some of the most common IP ports are: Table 34 Common IP Ports 21 FTP 53 DNS 23 Telnet 80 HTTP 25 SMTP 110 POP3 P-660H-Tx v2 User's Guide 113