ZyXEL P-660H-T1 v2 User Guide - Page 159
Over Allotment of Bandwidth, Configuring Summary
 |
View all ZyXEL P-660H-T1 v2 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 159 highlights
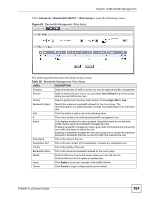
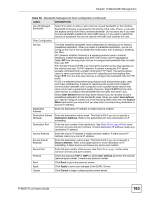
Chapter 12 Bandwidth Management 12.6.3 Bandwidth Management Priorities The following table describes the priorities that you can apply to traffic that the ZyXEL Device forwards out through an interface. Table 55 Bandwidth Management Priorities PRIORITY LEVELS: TRAFFIC WITH A HIGHER PRIORITY GETS THROUGH FASTER WHILE TRAFFIC WITH A LOWER PRIORITY IS DROPPED IF THE NETWORK IS CONGESTED. High Typically used for voice traffic or video that is especially sensitive to jitter (jitter is the variations in delay). Mid Typically used for "excellent effort" or better than best effort and would include important business traffic that can tolerate some delay. Low This is typically used for non-critical "background" traffic such as bulk transfers that are allowed but that should not affect other applications and users. 12.7 Over Allotment of Bandwidth You can set the bandwidth management speed for an interface higher than the interface's actual transmission speed. Higher priority traffic gets to use up to its allocated bandwidth, even if it takes up all of the interface's available bandwidth. This could stop lower priority traffic from being sent. The following is an example. Table 56 Over Allotment of Bandwidth Example BANDWIDTH CLASSES, ALLOTMENTS PRIORITIES Actual outgoing bandwidth available on the interface: 1000 kbps Root Class: 1500 kbps (same VoIP traffic (Service = SIP): 500 Kbps as Speed setting) NetMeeting traffic (Service = H.323): 500 kbps High High FTP (Service = FTP): 500 Kbps Medium If you use VoIP and NetMeeting at the same time, the device allocates up to 500 Kbps of bandwidth to each of them before it allocates any bandwidth to FTP. As a result, FTP can only use bandwidth when VoIP and NetMeeting do not use all of their allocated bandwidth. Suppose you try to browse the web too. In this case, VoIP, NetMeeting and FTP all have higher priority, so they get to use the bandwidth first. You can only browse the web when VoIP, NetMeeting, and FTP do not use all 1000 Kbps of available bandwidth. 12.8 Configuring Summary Click Advanced > Bandwidth MGMT to open the screen as shown next. Enable bandwidth management on an interface and set the maximum allowed bandwidth for that interface. P-660H-Tx v2 User's Guide 159