HP ProLiant xw2x220c Remote Graphics Software 5.3.0 User Guide - Page 37
The RGS Audio Player on the Local Computer, The RGS Audio Recorder captures the audio
 |
View all HP ProLiant xw2x220c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 37 highlights
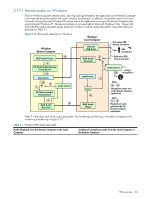
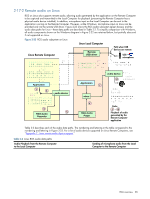
Table 2-1 Windows RGS audio data paths Audio Playback from the Remote Computer to the Local Computer Sending of microphone audio from the Local Computer to the Remote Computer 1. The application-generated audio output. USB devices are Local: 2. If an audio device is installed, the applicationgenerated audio is routed through it. a. The user selects the microphone source, either a USB microphone or an analog microphone. The RGS 3. If there is no audio device (such as with a blade Audio Recorder captures the selected microphone workstation), the HP Remote Audio virtual source. device is automatically installed, and the application-generated audio is routed to it. 4. Audio from either the audio device or the HP Remote Audio virtual device is sent to the RGS Audio Recorder. 5. The RGS Audio Recorder captures the audio, which is sent by RGS to the Local Computer. 6. The RGS Audio Player on the Local Computer decodes the received audio, and sends it to the b. The audio captured by the RGS Audio Recorder is sent by RGS to the RGS Audio Player on the Remote Computer. c. The RGS Audio Player decodes the audio signal, and sends it to the HP Remote Microphone virtual device. d. The HP Remote Microphone virtual device appears to the application as a local microphone, and sends the microphone audio to the application. audio mixer. USB devices are Remote: Beginning at RGS 5.2.0, certain 7. The output of the audio mixer is sent to the Local USB microphones can be mounted to the Remote Computer audio device. Computer using the remote USB driver-see Appendix B 8. The audio device drives an audio output device, for the supported microphones. See the previous section such as a speaker. for a description of Remote USB operation. RGS overview 37