Asus M3A78-EMH HDMI User Manual - Page 106
Choosing a RAID Level, RAID 0
 |
View all Asus M3A78-EMH HDMI manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 106 highlights
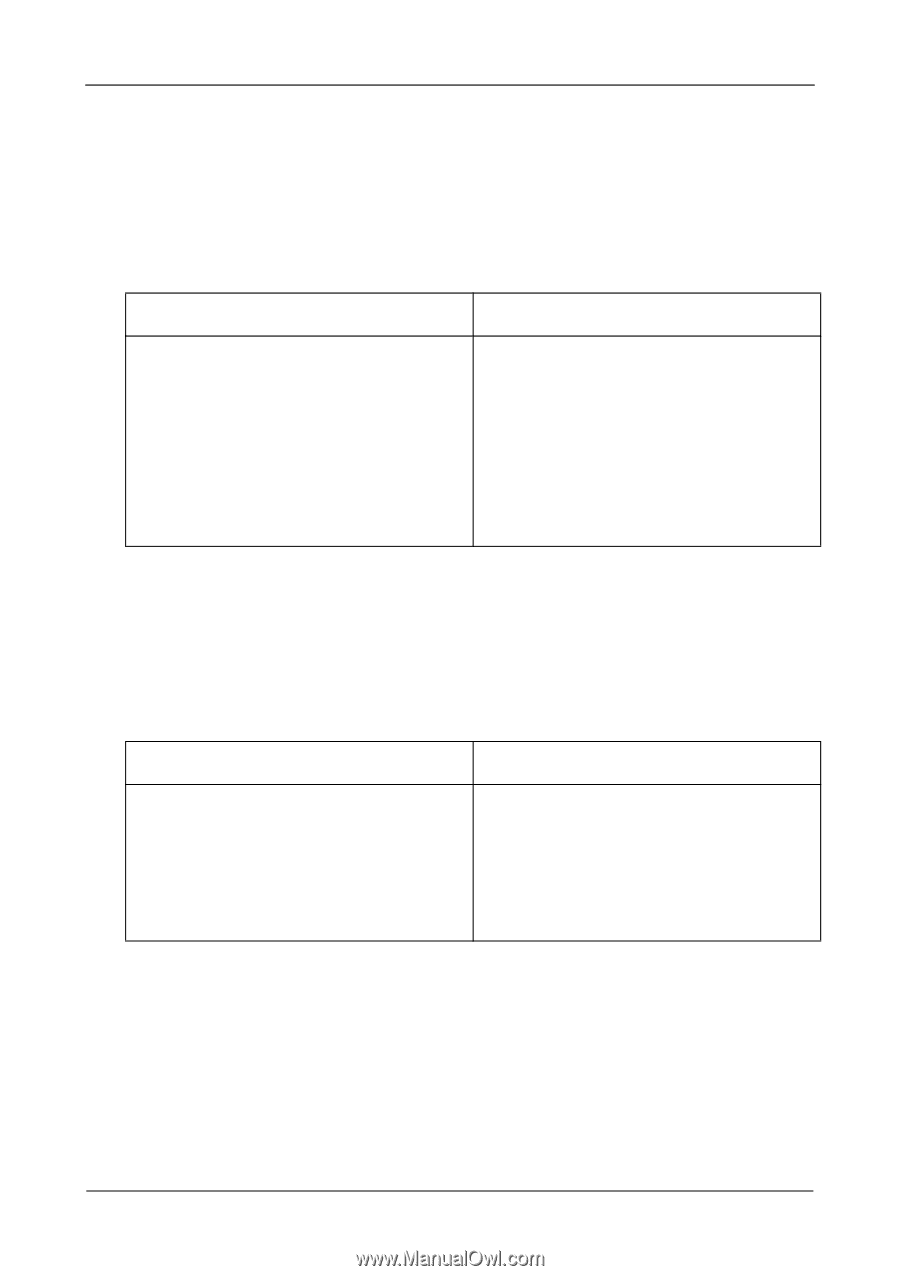
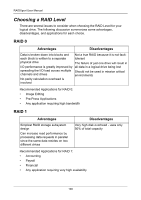
RAIDXpert User Manual Choosing a RAID Level There are several issues to consider when choosing the RAID Level for your logical drive. The following discussion summarizes some advantages, disadvantages, and applications for each choice. RAID 0 Advantages Disadvantages Data is broken down into blocks and Not a true RAID because it is not fault- each block is written to a separate tolerant physical drive The failure of just one drive will result in I/O performance is greatly improved by all data in a logical drive being lost spreading the I/O load across multiple Should not be used in mission critical channels and drives environments No parity calculation overhead is involved Recommended Applications for RAID 0: • Image Editing • Pre-Press Applications • Any application requiring high bandwidth RAID 1 Advantages Simplest RAID storage subsystem design Can increase read performance by processing data requests in parallel since the same data resides on two different drives Disadvantages Very high disk overhead - uses only 50% of total capacity Recommended Applications for RAID 1: • Accounting • Payroll • Financial • Any application requiring very high availability 100