Asus M3A78-EMH HDMI User Manual - Page 112
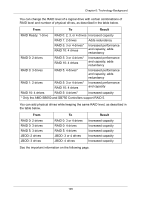
Ranges of Logical Drive Migration, than the Source logical drive
 |
View all Asus M3A78-EMH HDMI manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 112 highlights
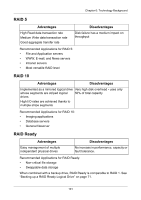
RAIDXpert User Manual Important • The Target logical drive may require more physical drives than the Source logical drive • If the Target logical drive requires an EVEN number of physical drives but the Source logical drive has an ODD number, ADD a physical drive as part of the migration process • You cannot reduce the number of physical drives in your logical drive • You cannot migrate a logical drive when it is Critical or performing activities such as Synchronizing or Rebuilding • You cannot migrate a JBOD to a RAID or a RAID to a JBOD Ranges of Logical Drive Migration There are limitations to how large you can expand a logical drive, depending on the size of your current logical drive. The Windows 2000 and Windows XP (32-bit) operating systems support a 10-byte LBA format. This means that a logical drive can have up to 4 billion address blocks or sectors. This limitation does not apply to Windows XP (64-bit), 2003 Server, Vista, and Linux OSes with the 2.6 kernel. For Windows 2000 and Windows XP (32-bit), multiply the number of blocks by the sector size to find the capacity of a logical drive: 4,000,000,000 blocks x 512 bytes per sector = 2,048,000,000,000 bytes of data for a 2TB drive. Note that you cannot change the size of the sectors nor can you increase the number of address blocks above 4 billion. As a result, there are range limits imposed upon logical drive migration as shown in the table above. For example: • You can migrate a 2.5 TB logical drive up to 4 TB • You can only migrate a 1.9 TB logical drive up to 2 TB 106