HP 4150 HP OmniBook 4150 - Reference Guide - Page 36
Operating the OmniBook, Reference Guide - omnibook specifications
 |
UPC - 725184276088
View all HP 4150 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 36 highlights
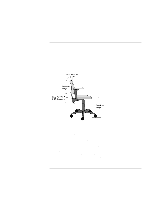
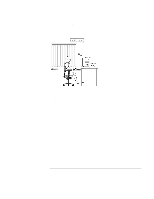
Operating the OmniBook Working in Comfort RSI has been a reported problem for those who perform repetitive tasks such as assembly line work, meatpacking, sewing, playing musical instruments, and computer work. RSI also has been observed in those who frequently engage in activities such as carpentry, knitting, housework, gardening, tennis, windsurfing and lifting children. What causes RSI? The specific causes of RSI have not been established. Nevertheless, the incidence of RSI has been associated with a variety of risk factors, including: • Too many uninterrupted repetitions of an activity or motion. • Performing an activity in an awkward or unnatural posture. • Maintaining static posture for prolonged periods. • Failing to take frequent short breaks. • Other environmental and psychosocial factors. In addition, there have been reports associating the occurrence of RSI with the use of computer keyboards, mice, and other input devices. Also, certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, obesity and diabetes, may predispose some people to this type of injury. What can I do to avoid RSI? Some people who use computers may experience physical discomfort during their use. This discomfort may be a symptom of a repetitive strain injury. Properly setting up and using computing equipment can help to minimize your chances of experiencing this discomfort. Well-designed and properly adjusted equipment alone may not be sufficient to eliminate all potential problems. Maintaining good posture and positioning when working on computers also has a significant bearing on your comfort. What if I experience discomfort? If you are experiencing any discomfort, seek professional medical advice immediately. Typically, the earlier a problem is diagnosed and treated, the easier it is to resolve. 36 Reference Guide