HP Integrity rx2800 HP Smart Update Manager User Guide - Page 108
Troubleshooting HP Smart Update Manager in IPv6 Windows Server 2008 environment
 |
View all HP Integrity rx2800 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 108 highlights
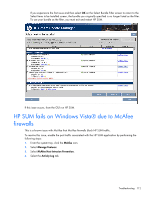
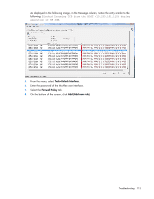
NOTE: You do not need to use the .ipv6-literal.net suffix when entering IPv6 address into the HP Smart Update Manager user interface or when passing IPv6 address using command line parameters to HP Smart Update Manager. After you validate that you can access the admin$ share on the remote target server, HP Smart Update Manager works unless other network or hardware issues exist. • Ensure you have made the registry change on remote target servers as mentioned in the HP Smart Update Manager Usage in a Windows Server® 2003 IPv6 environment ("Configuring IPv6 for Windows Server 2003" on page 92). • Move back to an IPv4 network address to ensure HP Smart Update Manager properly finds the remote target server without any issues. You can always copy HP Smart Update Manager to the target servers and execute using the local installation method. Troubleshooting HP Smart Update Manager in IPv6 Windows Server 2008 environment To validate that the IPv6 network is configured correctly for HP Smart Update Manager support, you must verify the following based on your operating system version. • Validate that you can ping the remote target server. With Windows® operating systems, you can use the ping command to ping IPv6 addresses: ping . • Ensure you can ping the IPv6 loopback address: ping ::1. • Use the DNS hostname instead of IPv6 address to ensure the address is correct. • Verify that you can connect to the admin$ share using the credentials within HP Smart Update Manager by issuing the following command at a console prompt: net use * \\.ipv6-literal.net\admin$ /user: net use * \\fec0::2.ipv6-literal.net\admin$ /user:administrator You might need to provide the password if you use a user name that is different from the one you used to log in to the local system. All network shares require the use of the .ipv6-literal.net name string to be properly configured by Windows®. After you validate you can access the admin$ share on the remote target server, HP Smart Update Manager works unless there are other network or hardware issues. Troubleshooting HP Smart Update Manager in IPv6 Red Hat and Novell SUSE-based Linux environments • Verify that you can establish an SSH connection to the remote target server using the credentials within HP Smart Update Manager by issuing the following command at a console prompt: ssh SSh 2101:db8:0:1::9 You must enter the root password for the target Linux server at the console to complete the IPv6 connection. • Validate that you can ping the remote target server. In Linux, you need to use the ping6 command to ping IPv6 addresses: ping6 . Troubleshooting 108