HP ProLiant DL280 Configuring Arrays on HP Smart Array Controllers Reference G - Page 32
Rapid Parity Initialization, Default, Rapid
 |
View all HP ProLiant DL280 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 32 highlights
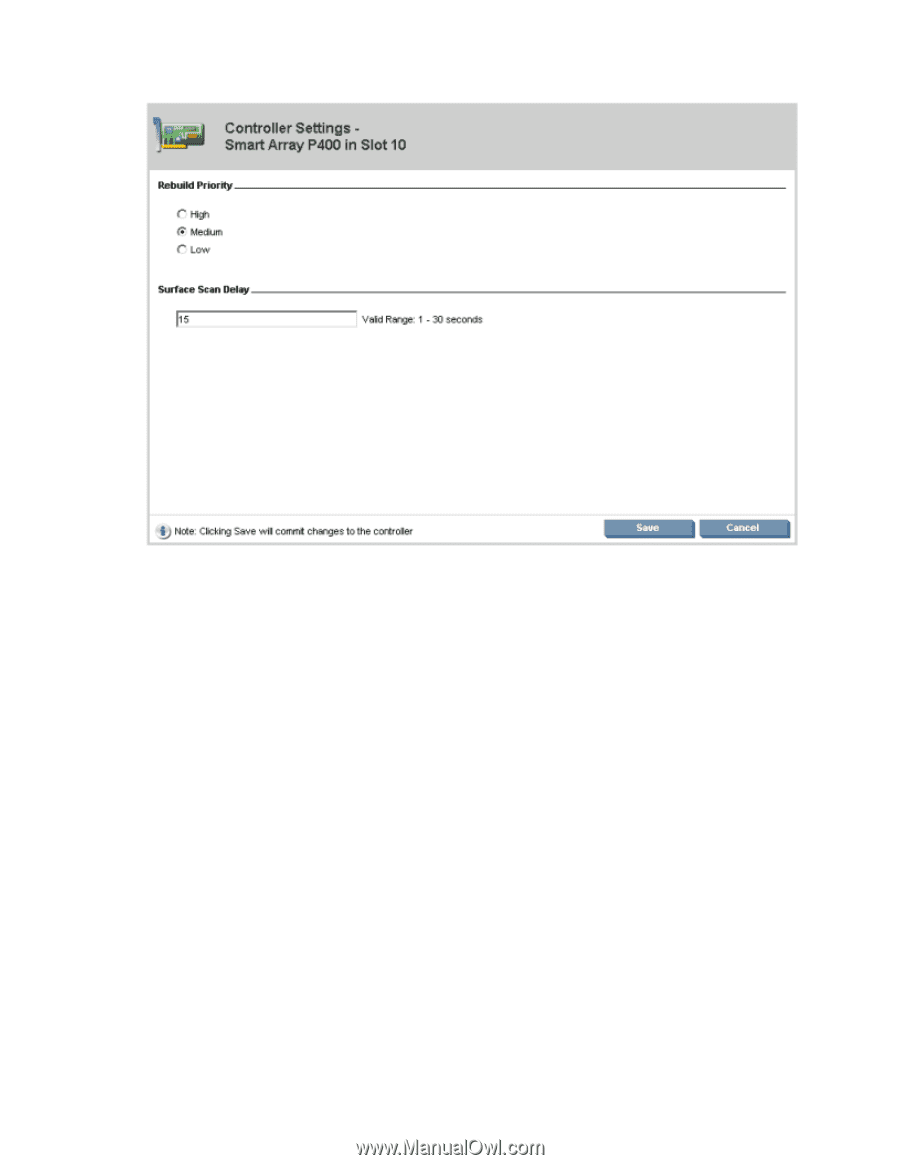
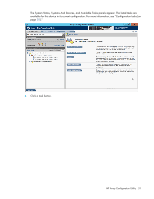
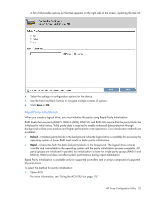
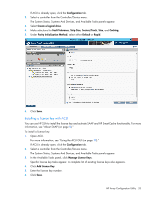
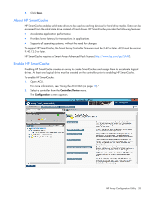
A list of all possible options for that task appears on the right side of the screen, replacing the task list. 4. Select the settings or configuration options for the device. 5. Use the Next and Back buttons to navigate multiple screens of options. 6. Click Save or OK. Rapid Parity Initialization When you create a logical drive, you must initialize the parity using Rapid Parity Initialization. RAID levels that use parity (RAID 5, RAID 6 (ADG), RAID 50, and RAID 60) require that the parity blocks be initialized to valid values. Valid parity data is required to enable enhanced data protection through background surface scan analysis and higher performance write operations. Two initialization methods are available: • Default - Initializes parity blocks in the background while the logical drive is available for access by the operating system. A lower RAID level results in faster parity initialization. • Rapid - Overwrites both the data and parity blocks in the foreground. The logical drive remains invisible and unavailable to the operating system until the parity initialization process completes. All parity groups are initialized in parallel, but initialization is faster for single parity groups (RAID 5 and RAID 6). RAID level does not affect system performance during rapid initialization. Rapid Parity Initialization is available only for supported controllers and in arrays composed of supported physical drives. To select the method for parity initialization: 1. Open ACU. For more information, see "Using the ACU GUI (on page 19)." HP Array Configuration Utility 32