HP rp3440 HP Integrity and HP 9000 iLO MP Operations Guide, Fifth Edition - Page 120
Creating Roles that Follow Organizational Structure, Restricting Roles, Role Time Restrictions
 |
View all HP rp3440 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 120 highlights
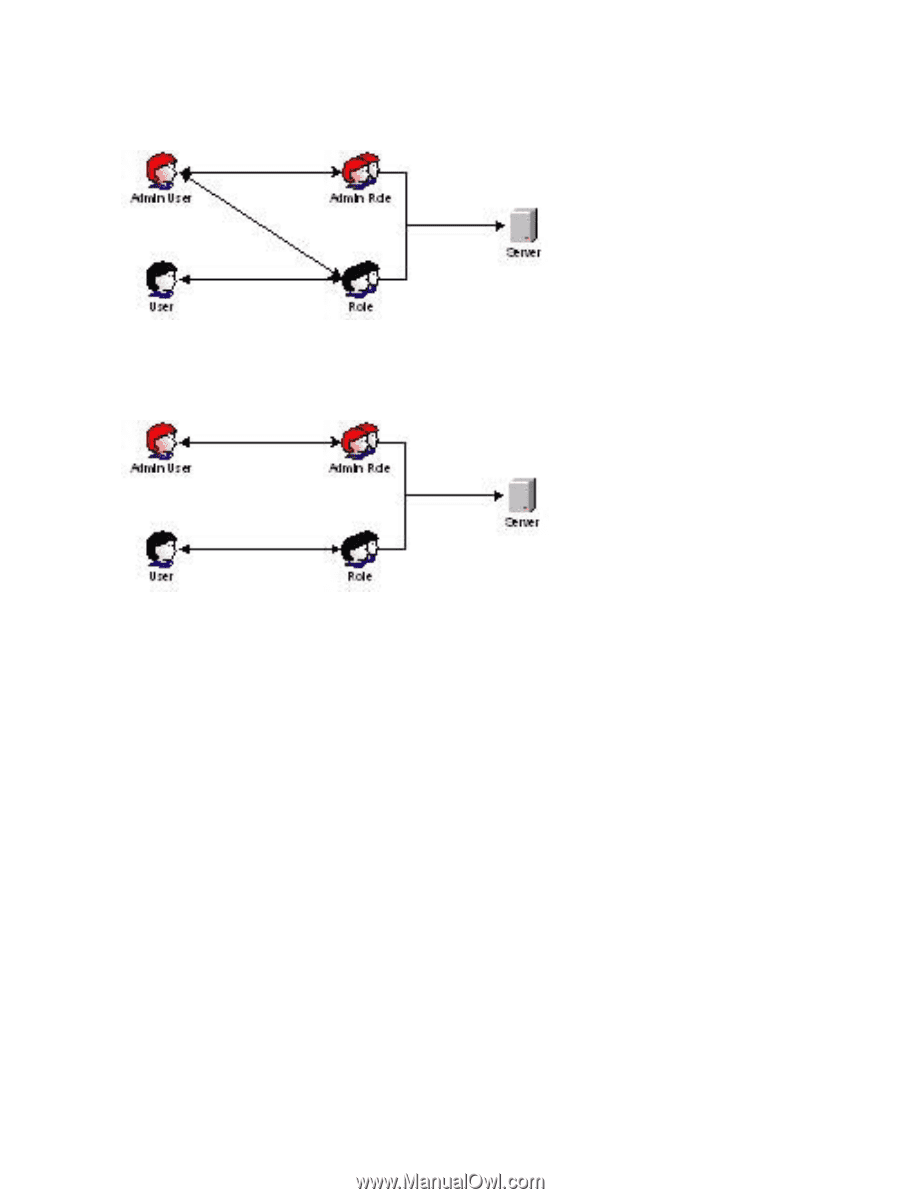
The following figure shows one way that an administrative user gains Admin Role right. The Admin User's initial login right is granted through the regular user role. After the initial login, more advanced rights are assigned to the Admin User through the Admin Role such as Server Reset and Remote Console. In the following figure, the Admin User gains the Admin Role right in a different way. The Admin User initially logs in through the Admin Role and is assigned admin rights such as Server Reset, Remote Console, and Login. Creating Roles that Follow Organizational Structure Often, administrators within an organization are placed into a hierarchy in which subordinate administrators must assign rights independently of ranking administrators. In this case, it is useful to have one role that represents the rights assigned by higher-level administrators, and to allow subordinate administrators to create and manage their own roles. Restricting Roles Restrictions enable you to limit the scope of a role. A role only grants rights to those users who satisfy the role's restrictions. Using restricted roles creates users with dynamic rights that change based on the time of day or network address of the client. For step-by-step instructions on how to create network and time restrictions for a role, see "Setting Role Restrictions" (page 112) or "Setting Time Restrictions" (page 112). Role Time Restrictions You can place time restrictions on iLO MP roles. Users are only granted rights that are specified for the iLO MP devices listed in the role, only if they are members of the role and meet the time restrictions for that role. iLO MP devices use local host time to enforce time restrictions. If the iLO MP device clock is not set, the role time restriction fails unless no time restrictions are specified on the role. Role-based time restrictions can only be satisfied if the time is set on the iLO MP device. The time is normally set when the host is booted, and is maintained by running the agents in the host operating system, which enables the iLO MP device to compensate for leap years and minimize clock drift with respect to the host. Events such as unexpected power loss or the flashing of iLO 120 Installing and Configuring Directory Services