Netgear WNDAP660 Reference Manual - Page 9
Key Features, STP and LLDP - support
 |
View all Netgear WNDAP660 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 9 highlights
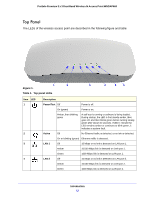
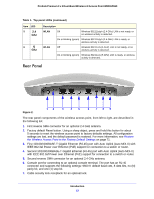
ProSafe Premium 3 x 3 Dual-Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP660 • DHCP server and client. The DHCP server of the wireless access point can provide a dynamic IPv4 or IPv6 address to wireless clients. The wireless access point can also act as a client and obtain an IPv4 or IPv6 address from a DHCP server on the LAN. • SNMP. The wireless access point supports Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) for Management Information Base (MIB) management. • STP and LLDP. The wireless access point supports Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and Ethernet Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP). LLDP is enabled by default. • 802.1Q VLAN. A network of computers can behave as if they are connected to the same network even though they might actually be physically on different segments of a LAN. Virtual LANs (VLANs) are configured through software rather than hardware, which makes them very flexible. VLANs are very useful for user and host management, bandwidth allocation, and resource optimization. Key Features The wireless access point provides solid functionality, including the following features: • Dual band. The wireless access point can operate concurrently in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. • Band steering. Band steering can ensure that a dual-band wireless station operates in the 5 GHz band rather than in the 2.4 GHz band, which is often highly congested. Band steering can also move a wireless station that already operates in the 2.4 GHz band to the 5 GHz band. Band steering is an advanced wireless feature that reduces the client density in the 2.4 GHz band and increases the wireless network capacity. • IPv4 and IPv6. The wireless access point is manageable from either an IPv4 or IPv6 address, it can function as an IPv4 or IPv6 DHCP client, and its DHCP server can allocate either IPv4 or IPv6 addresses. • Multiple operating modes: - Wireless access point. Operates as a standard 802.11b/g/n and 802.11a/n wireless access point. - Point-to-point bridge. In this mode, the wireless access point communicates only with another bridge-mode wireless station or wireless access point. Network authentication should be used to protect this communication. - Point-to-multipoint bridge. Select this option only if this wireless access point is the master for a group of bridge-mode wireless stations. The other bridge-mode wireless stations send all traffic to this master and do not communicate directly with each other. Network authentication should be used to protect this traffic. - Repeater. In this mode, the wireless access point does not function as an access point for clients but functions only in point-to-multipoint bridge mode to repeat the wireless signal and send all traffic to a remote access point. Network authentication should be used to protect this communication. • WMM. Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) is a subset of the 802.11e standard. WMM allows wireless traffic to have a range of priorities, depending on the kind of data. Time-dependent information, like video or audio, has a higher priority than normal traffic. For WMM to function correctly, wireless clients also need to support WMM. Introduction 9