TP-Link EAP245 EAP Controller V2.4.7 User Guide - Page 7
Determine the Network Topology, Manage EAPs in the LAN, Manage EAPs in Different Network Segment
 |
View all TP-Link EAP245 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 7 highlights
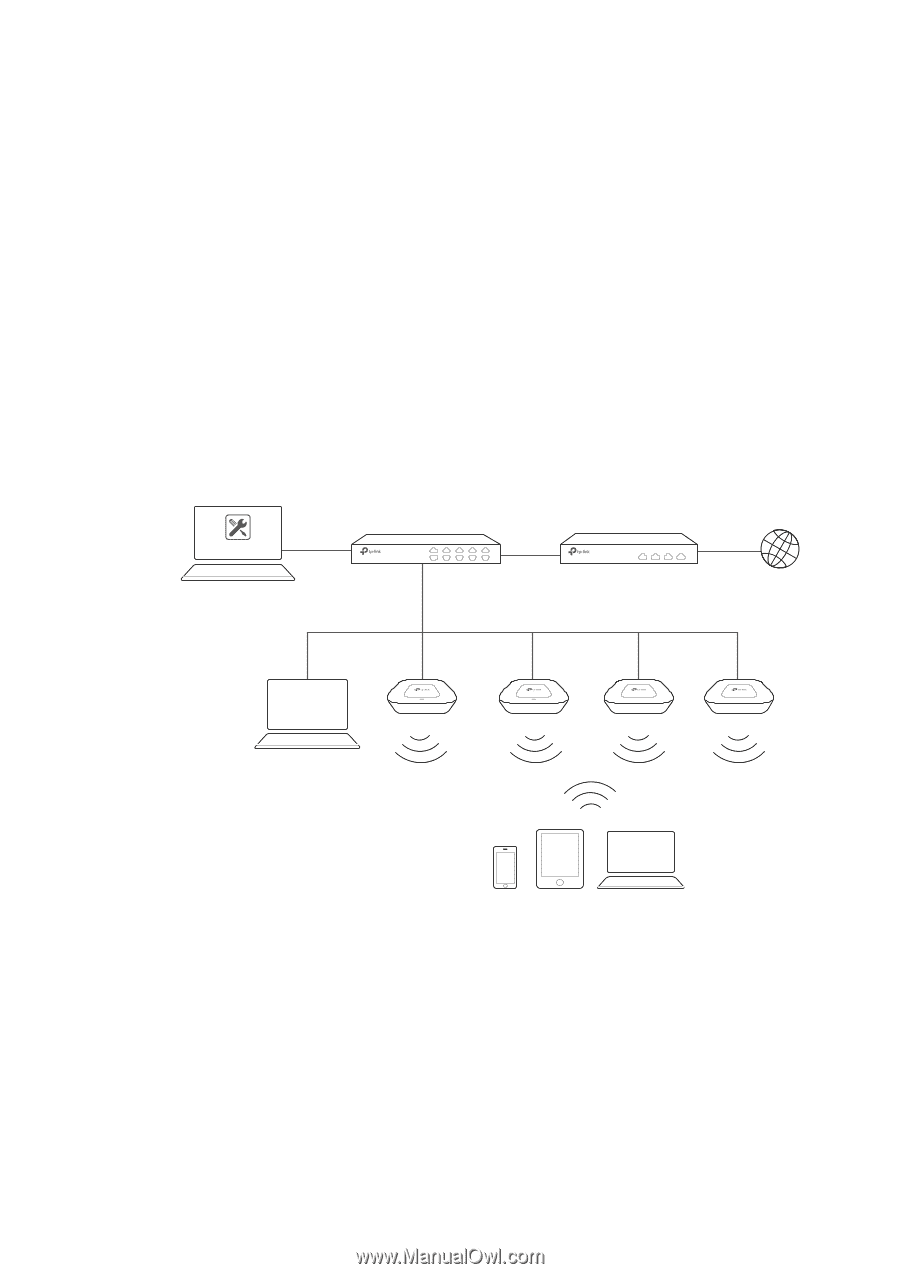
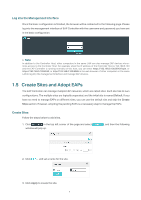
1.1 Determine the Network Topology You can use the EAP Controller to centrally manage the EAPs in same or different network segment. Manage EAPs in the LAN If you want to manage the EAPs with a host in the LAN, refer to the following network topology. A router acts as a DHCP server to assign IP addresses to EAPs and clients. In the LAN, only one host needs to install EAP Controller. The host is called as Controller Host. And the other hosts in the same LAN can access the Controller Host to manage the network. In this topology, you can visit EAP Controller interface from Host B by entering "192.168.0.100: 8043" in a web browser. It's recommended to set a static IP address to the Controller Host for the convenient login to the EAP Controller interface. Host A (Controller Host) IP: 192.168.0.100 Switch Router (DHCP Server) LAN IP:192.168.0.1 Internet EAP Controller Host B IP: 192.168.0.200 EAPs Clients // Not: The EAP Controller must be running all the time when you manage the network. Manage EAPs in Different Network Segment If the Controller Host needs to manage EAPs in different network segment, refer to the following topology. A router acts as a DHCP server to assign IP addresses to EAPs and clients. The Controller Host and the EAP devices are connected to the Router's different network segments. To help the EAPs find the Controller Host and be managed, EAP Discover Utility should be installed in the Host B which is 2