TP-Link T2700G-28TQ T2700G-28TQ User Guide V1 - Page 188
OSPF (License Required), Steps, Operation, Routing, Basic Config, Introduction
 |
View all TP-Link T2700G-28TQ manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 188 highlights
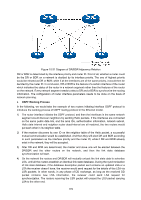
Configure Switch B Steps Operation Note 1 Enable RIP Required. On page Routing→ RIP→ Basic Config, enable RIP, select RIPv2 as RIP version. 2 Enable the network Required. On page Routing→ RIP→ Basic Config Network segments where Enable part, add network segments 1.1.1.0, 10.1.1.0, 11.1.1.0, and the interfaces are enable RIP in these network segments. These network segments located will be displayed in RIP Network List after they are successfully added. 10.9 OSPF (License Required) OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) is a routing protocol based on link state and also an internal gateway protocol, which is developed and recommended by IETF. The OSPF protocol standard in current use for IPv4 network is OSPF Version 2, which is defined specifically in RFC2328 and will be introduced generally in this Guide. Introduction 1. OSPF Features OSPF protocol is a popular routing protocol in networking with the following features. Fast convergence - It could send update packets immediately upon the change of network topology, to quickly synchronize the update for the routers in the autonomous system. Due to the rapid convergence, OSPF routing protocol acts with great speediness and stability in the large-scale network, and is not prone to some harmful routing information. OSPF protocol introduces the concept of area - to manage the autonomous system by area, which means the routers only need to synchronize the link state database with the other routers in the same area. Thus, the smaller link state database requires lower memory consumption from the routers, and the less routing information to manage also releases certain CPU resources for the routers and meanwhile reduces the network bandwidth occupied by the routing information. OSPF protocol supports multiple equal-cost routes to one destination for load balance, thus to perform more efficient data forwarding. OSPF supports VLSM route addressing by variable-length subnet mask. OSPF supports the message authentication based on interfaces, thus to guarantee the security of message interaction and routing calculation. OSPF supports using the reserved multicast address in the link of specific network type, to reduce the influence on the other irrelevant routers. 2. OSPF Common Scenario OSPF protocol is usually applied in the large complex network environment. Shown as below is the instance diagram of a large company, where the large network is divided by department. OSPF protocol works as the fundamental routing protocol among routers, which could guarantee not only the message interaction but also the network independence among departments. 176