TP-Link T2700G-28TQ T2700G-28TQ User Guide V1 - Page 224
Typical Networking Application Diagram, VRRP Operating Principle
 |
View all TP-Link T2700G-28TQ manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 224 highlights
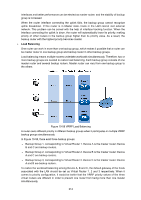
still be provided and network interruption can be avoided after a single link fails without reconfiguration of dynamic routing or router discovery protocols, or default gateway configuration on every end-host. 2. Small network overhead. The single message that VRRP defines is the VRRP advertisement, which can only be sent by the master router. Typical Networking Application Diagram Figure 10-57 Typical Networking Application Diagram VRRP Operating Principle 1. Working Process VRRP backup group, or virtual router, consists of a group of physical routers with the same VRID (virtual route identifier). A virtual router owns one or more virtual IP addresses and one virtual MAC address, in the format 00-00-5E-00-01-{VRID}. The IP address of the virtual router is assigned as the default gateway for the hosts within the LAN. Communication with external network can be realized via the virtual router. Master router is selected from the physical routers in the virtual router group according to VRRP priority. The elected master router provides routing service to the hosts in LAN, and sends VRRP messages periodically to publicize its configuration information like priority and operating condition to other routers in backup group. Other physical routers in the backup group work as backup routers. They monitor the VRRP packets sent by the master router. A new master router will be elected among them to take the role of the master router if master router fails. 2. Master Election Initially-created routers work in Backup state and learn other members' priorities in the virtual router via VRRP packets. The one with the highest priority is elected as master router. If the priority values are the same, the router with the highest interface IP address is selected as the master. • In preemptible mode, when backup router receives VRRP packet, it will compare its priority with that of the advertisement packet. If of higher priority, the backup router will become the master router; otherwise, it will maintain Backup state. • In non-preemptible mode, physical routers in the backup group will maintain Master or Backup state as long as the master router functions normally. Even if backup router is given higher priority, it cannot become a master router in non-preempt mode. 212