Cisco AIR-AP1242AG-E-K9 Hardware Installation Guide - Page 25
Repeater Unit that Extends Wireless Range, Point-to-Point Bridge Configuration
 |
View all Cisco AIR-AP1242AG-E-K9 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 25 highlights
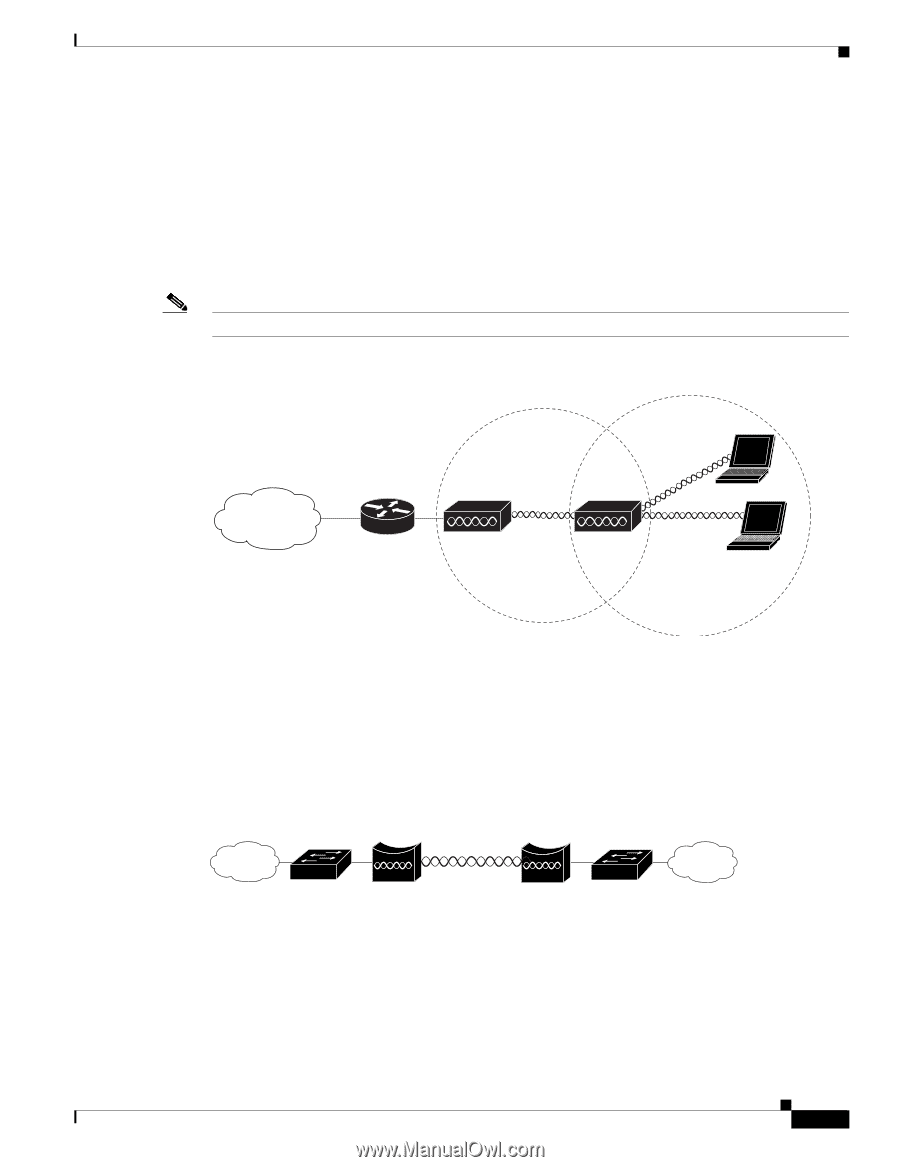
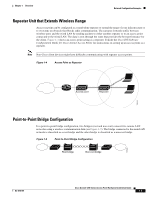
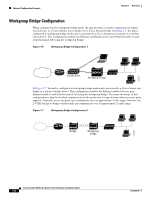
Chapter 1 Overview Network Configuration Examples Repeater Unit that Extends Wireless Range An access point can be configured as a stand-alone repeater to extend the range of your infrastructure or to overcome an obstacle that blocks radio communication. The repeater forwards traffic between wireless users and the wired LAN by sending packets to either another repeater or to an access point connected to the wired LAN. The data is sent through the route that provides the best performance for the client. Figure 1-4 shows an access point acting as a repeater. Consult the Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide for Cisco Aironet Access Points for instructions on setting up an access point as a repeater. Note Non-Cisco client devices might have difficulty communicating with repeater access points. Figure 1-4 Access Point as Repeater Access point Repeater 135444 Point-to-Point Bridge Configuration In a point-to-point bridge configuration, two bridges (root and non-root) connect two remote LAN networks using a wireless communication link (see Figure 1-5). The bridge connected to the main LAN network is classified as a root bridge and the other bridge is classified as a non-root bridge. Figure 1-5 Point-to-Point Bridge Configuration 117029 Root bridge Non-root bridge OL-4310-05 Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Point Hardware Installation Guide 1-7