Garmin Forerunner 301 Owner's Manual - Page 50
Appendix, Training with Heart Rate Zones
 |
UPC - 753759047290
View all Garmin Forerunner 301 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 50 highlights
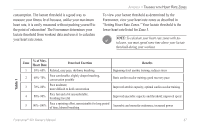
APPENDIX > TRAINING WITH HEART RATE ZONES APPENDIX Training with Heart Rate Zones Many runners, bikers, and other athletes are using heart rate "zones" to measure and increase their cardiovascular strength and improve their level of fitness. What are heart rate zones? A heart rate zone is simply a range of heartbeats per minute (bpm). The five commonly accepted heart rate zones are numbered from 1-5 according to increasing intensity. Generally, heart rate zones are calculated based on percentages of your maximum heart rate. See Table 1 to learn some of the effects of exercise as your heart rate reaches each of these zones during a workout. How do heart rate zones help you achieve fitness goals? Knowing your heart rate zones can help you measure and improve your fitness by knowing and applying these principles: 46 • Your heart rate is a good measure of workout intensity. • Training in certain heart rate zones can help you improve cardiovascular capacity and strength. • Knowing your heart rate zone can prevent you from overtraining and decrease your risk of injury. See Table 1 to learn the benefits of training in each heart rate zone. How does the Forerunner determine my heart rate zones? If you know your maximum heart rate, you can enter it and allow the Forerunner to calculate your heart rate zones based on the percentages shown in Table 1 (see "Setting HR Zones Manually" in the Customizing section). However, the Forerunner 301 has a built-in feature called AutoLearn, which determines your heart rate zones automatically and continues to adjust them as your fitness level improves. To determine your heart rate zones, the Forerunner pinpoints your lactate threshold-the point where your body switches from aerobic energy consumption to anaerobic energy Forerunner® 301 Owner's Manual