Intel AFCSASRISER User Guide - Page 26
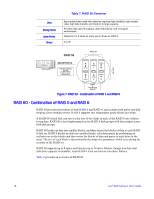
RAID 10 - Combination of RAID 1 and RAID 0, Table 5. RAID 1E Overview
 |
View all Intel AFCSASRISER manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 26 highlights
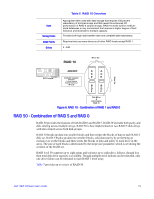
Figure 5. Integrated Mirroring Enhanced with Three Disks Uses Strong Points Weak Points Drives Table 5. RAID 1E Overview Use RAID 1E for small databases or any other environment that requires fault tolerance but small capacity. Provides complete data redundancy. RAID 1E is ideal for any application that requires fault tolerance and minimal capacity. Requires twice as many disk drives. Performance is impaired during drive rebuilds. 3 to 10 RAID 10 - Combination of RAID 1 and RAID 0 RAID 10 is a combination of RAID 0 and RAID 1. RAID 10 consists of stripes across mirrored drives. RAID 10 breaks up data into smaller blocks and then mirrors the blocks of data to each RAID 1 RAID set. Each RAID 1 RAID set then duplicates its data to its other drive. The size of each block is determined by the stripe size parameter, which is set during the creation of the RAID set. RAID 10 supports up to eight spans. Table 6 provides an overview of RAID 10. 14 Intel® RAID Software User's Guide