HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch FCoE Configuration Guide - Page 13
How FCoE works, Procedure for receiving and sending FC frames over Ethernet
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 13 highlights
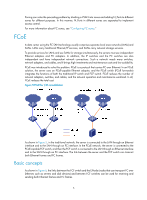
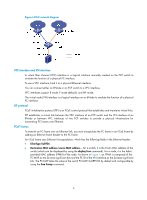
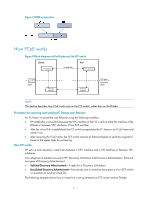
Figure 7 FPMA composition How FCoE works Figure 8 Block diagrams of the ENode and the FCF switch ENode VN interface Virtual link FCF VFC interface FC layer Ethernet layer Ethernet interface Ethernet interface FC layer Ethernet layer NOTE: This section describes how FCoE works only on the FCF switch, rather than on the ENode. Procedure for receiving and sending FC frames over Ethernet An FC frame is transmitted over Ethernet using the following workflow: • FIP establishes a virtual link between the VFC interface of the FCF switch and the VN interface of the ENode or between VFC interfaces of two FCF switches. • After the virtual link is established, the FCF switch encapsulates the FC frame in an FCoE frame and sends it out. • After receiving the FCoE frame, the FCF switch removes its Ethernet header to send the original FC frame to the upper layer for processing. How FIP works FIP sets up and maintains virtual links between a VFC interface and a VN interface or between VFC interfaces. Two categories of packets are used in FIP: Discovery Solicitation and Discovery Advertisement. There are two types of Discovery Advertisement: • Solicited Discovery Advertisement-A reply for a Discovery Solicitation. • Unsolicited Discovery Advertisement-Periodically sent to advertise the presence of an FCF switch or maintain an existing virtual link. The following example shows how a virtual link is set up between an FCF switch and an ENode. 7