HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch FCoE Configuration Guide - Page 77
Configuring FC zones, Overview, Zone database, Zone database structure
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 77 highlights
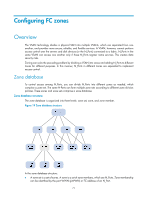
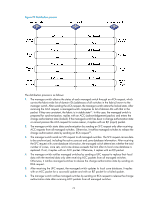
Configuring FC zones Overview The VSAN technology divides a physical SAN into multiple VSANs, which are separated from one another, and provides more secure, reliable, and flexible services. A VSAN, however, cannot perform access control over the servers and disk devices (or the N_Ports) connected to a fabric. N_Ports in the same VSAN can access one another only if these N_Ports register name services. This creates data security risks. Zoning can solve the preceding problem by dividing a VSAN into zones and adding N_Ports to different zones for different purposes. In this manner, N_Ports in different zones are separated to implement access control. Zone database To control access among N_Ports, you can divide N_Ports into different zones as needed, which comprise a zone set. The same N-Ports can form multiple zone sets according to different zone division policies. These zones and zone sets comprise a zone database. Zone database structure The zone database is organized into three levels: zone set, zone, and zone member. Figure 19 Zone database structure In the zone database structure: • A zone set is a set of zones. A zone is a set of zone members, which are N_Ports. Zone membership can be identified by the port WWN (pWWN) or FC address of an N_Port. 71