Netgear DG834G DG834Gv5 Reference Manual - Page 157
Step-By-Step Configuration, dg834g.dyndns.org, admin, password
 |
UPC - 606449029918
View all Netgear DG834G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 157 highlights
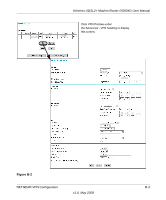
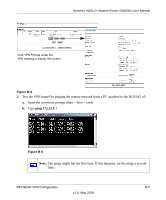
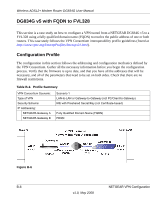
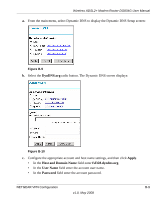
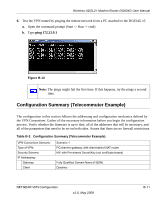
Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DG834G User Manual Note: Product updates are available on the NETGEAR website at http://www.netgear.com. Using a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) Many ISPs (Internet Service Providers) provide connectivity to their customers using dynamic instead of static IP addressing. This means that a user's IP address does not remain constant over time, which presents a challenge for gateways attempting to establish VPN connectivity. A Dynamic DNS (DDNS) service allows a user whose public IP address is dynamically assigned to be located by a host or domain name. It provides a central public database where information (such as e-mail addresses, host names, and IP addresses) can be stored and retrieved. Now, a gateway can be configured to use a third-party service in lieu of a permanent and unchanging IP address to establish bi-directional VPN connectivity. To use DDNS, you must register with a DDNS service provider. Some DDNS service providers include: • DynDNS: www.dyndns.org • TZO.com: netgear.tzo.com • ngDDNS: ngddns.iego.net In this example, Gateway A is configured using an example FQDN provided by a DDNS Service provider. In this case we established the hostname dg834g.dyndns.org for Gateway A using the DynDNS service. Gateway B uses the DDNS service provider when establishing a VPN tunnel. To establish VPN connectivity, Gateway A must be configured to use Dynamic DNS, and Gateway B must be configured to use a DNS host name provided by a DDNS service provider to find Gateway A. Again, the following step-by-step procedures assume that you have already registered with a DDNS service provider and have the configuration information necessary to set up the gateways. Step-By-Step Configuration 1. Log in to the DG834G v5 labeled Gateway A as in the illustration. Out of the box, the DG834G v5 is set for its default LAN address of http://192.168.0.1 with its default user name of admin, and default password of password. This example assumes that you have set the local LAN address as 10.5.6.1 for Gateway A and have set your own password. 2. On the DG834G v5, configure the Dynamic DNS settings. NETGEAR VPN Configuration B-7 v1.0, May 2008