Netgear DG834G DG834Gv5 Reference Manual - Page 25
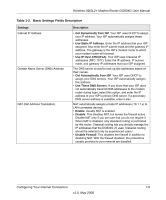
Table 1-2., Basic Settings Fields Description, Configuring Your Internet Connection - v5
 |
UPC - 606449029918
View all Netgear DG834G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 25 highlights
Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DG834G User Manual Table 1-2. Basic Settings Fields Description Settings Internet IP Address Domain Name Server (DNS) Address NAT (Net Address Translation) Description • Get Dynamically from ISP. Your ISP uses DHCP to assign your IP address. Your ISP automatically assigns these addresses. • Use Static IP Address. Enter the IP address that your ISP assigned. Also enter the IP subnet mask and the gateway IP address. The gateway is the ISP's modem router to which your modem router will connect. • Use IP Over ATM (IFoA). Your ISP uses Classical IP addresses (RFC 1577). Enter the IP address, IP subnet mask, and gateway IP addresses that your ISP assigned. The DNS server is used to look up site addresses based on their names. • Get Automatically from ISP. Your ISP uses DHCP to assign your DNS servers. Your ISP automatically assigns this address. • Use These DNS Servers. If you know that your ISP does not automatically transmit DNS addresses to the modem router during login, select this option, and enter the IP address of your ISP's primary DNS server. If a secondary DNS server address is available, enter it also. NAT automatically assigns private IP addresses (10.1.1.x) to LAN-connected devices. • Enable. Usually NAT is enabled. • Disable. This disables NAT, but leaves the firewall active. Disable NAT only if you are sure that you do not require it. When NAT is disabled, only standard routing is performed by this router. Classical routing lets you directly manage the IP addresses that the DG834G v5 uses. Classical routing should be selected only by experienced users.a • Disable Firewall. This disables the firewall in addition to disabling NAT. With the firewall disabled, the protections usually provided to your network are disabled. Configuring Your Internet Connection 1-9 v1.0, May 2008