Sony VGX-XL1 User Guide - Page 134
Improved Availability, Increased and Integrated Capacity, Improved Performance, RAID Levels (Types)
 |
View all Sony VGX-XL1 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 134 highlights
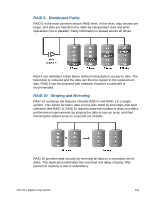
Improved Availability Availability refers to your data being present and ready to use. A RAID system improves availability by providing fault tolerance and by providing special features that allow for recovery from hardware faults without disruption. Increased and Integrated Capacity RAID systems increase capacity by turning a number of smaller drives into a larger array, thus combining or adding their individual storage capacities together. This facilitates applications that require large amounts of contiguous disk space, and also makes disk space management simpler. (However, a percentage of total capacity is lost to overhead or redundancy in most implementations.) Improved Performance RAID systems improve performance by allowing the controller to take full advantage of the capabilities of multiple hard disk to get around performancelimiting issues that plague individual hard disks. Different RAID implementations improve performance in different ways and to different degrees, but all improve performance in some way. RAID Levels (Types) Currently, Sony supports four different levels or types of RAID to implement an array, using combinations of mirroring, striping, duplexing, and parity technologies. Each RAID level is independent and different, and no strict hierarchy should be inferred from the specific number attached to a RAID level. In other words, a RAID level that is "better" for one person may be "worse" for another. Note: The software to perform the RAID-functionality and control the hard disks can simply be a driver, or can be located on a separate hardware RAID controller. Some Microsoft® operating systems include a software RAID solution for a lower cost option. Hardware RAID controllers cost more than pure software, but can offer better performance. What are the different RAID Levels? A RAID array is made up of two or more hard disks working in parallel, which appear and function as a single hard disk to the user. Sony has approved four different RAID levels or types for use in VAIO® computers. VGX-XL1 Digital Living System 131