Sony VGX-XL1 User Guide - Page 136
RAID 5 - Distributed Parity, RAID 10 - Striping and Mirroring
 |
View all Sony VGX-XL1 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 136 highlights
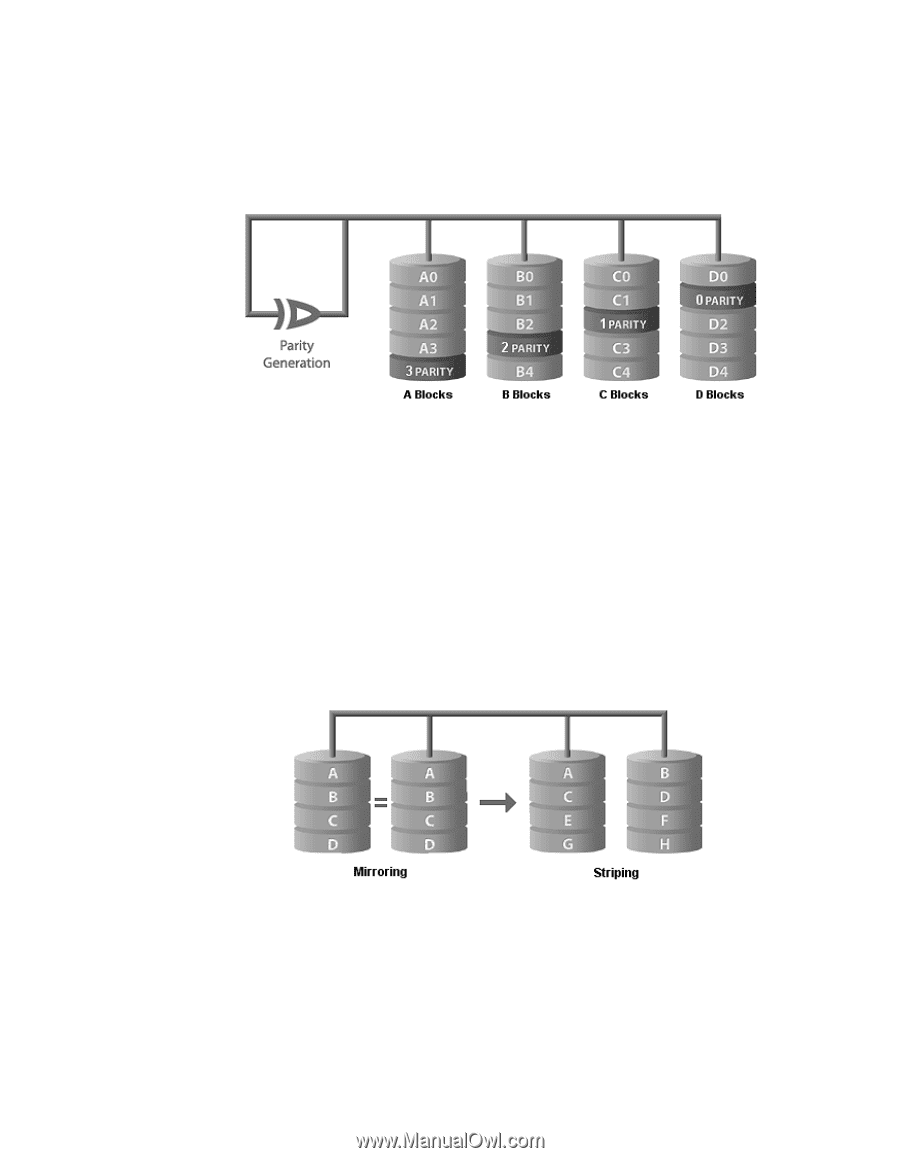
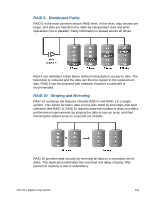
RAID 5 - Distributed Parity RAID 5 is the most common secure RAID level. In this level, data chunks are larger, and data are transferred to disks by independent read and write operations (not in parallel). Parity information is spread across all drives. Raid 5 can withstand a disk failure without losing data or access to data. The failed disk is removed and the data can then be copied to the replacement disk. RAID 5 can be achieved with software, however a controller is recommended. RAID 10 - Striping and Mirroring RAID 10 combines the features of levels RAID 0 and RAID 1 in a single system. This allows for faster data access (like RAID 0) and single-disk fault tolerance (like RAID 1). RAID 10 requires twice the number of disks, but offers performance improvements by striping the data across an array, and then mirroring the striped array on a second set of disks. RAID 10 provides data security by mirroring all data on a secondary set of disks. This duplication eliminates the overhead and delay of parity. Fifty percent of capacity is lost to redundancy. VGX-XL1 Digital Living System 133