TP-Link 10GE T1700G-28TQUN V1 User Guide - Page 209
DHCP Snooping
 |
View all TP-Link 10GE manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 209 highlights
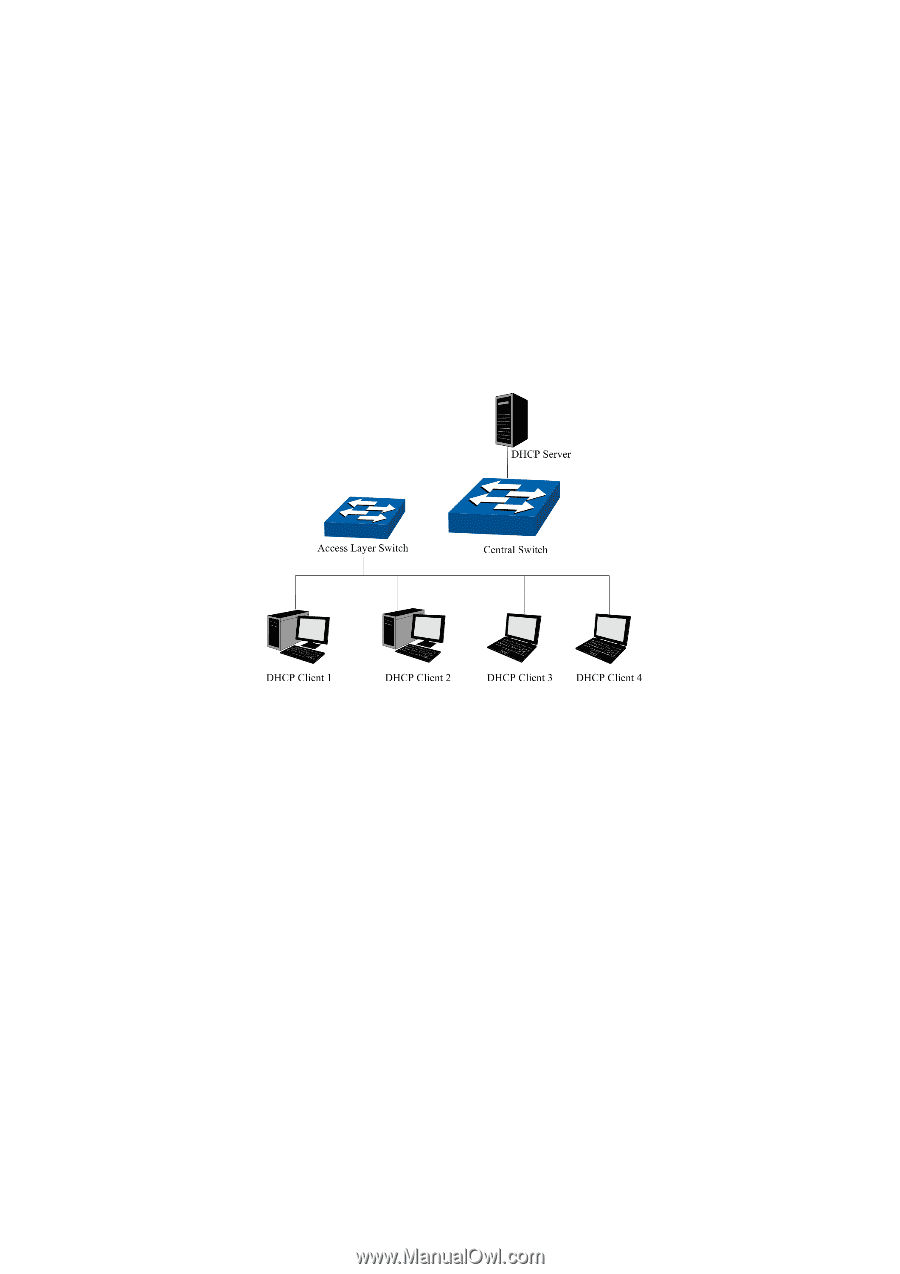
13.2 DHCP Snooping Nowadays, the network is getting larger and more complicated. The amount of the PCs always exceeds that of the assigned IP addresses. The wireless network and the laptops are widely used and the locations of the PCs are always changed. Therefore, the corresponding IP address of the PC should be updated with a few configurations. DHCP(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, the network configuration protocol optimized and developed basing on the BOOTP, functions to solve the above mentioned problems. DHCP Working Principle DHCP works via the "Client/Server" communication mode. The Client applies to the Server for configuration. The Server assigns the configuration information, such as the IP address, to the Client, so as to reach a dynamic employ of the network source. A Server can assign the IP address for several Clients, which is illustrated in the following figure. Figure 13-5 Network diagram for DHCP-snooping implementation For different DHCP Clients, DHCP Server provides three IP address assigning methods: (1) Manually assign the IP address: Allows the administrator to bind the static IP address to the specific Client (e.g.: WWW Server) via the DHCP Server. (2) Automatically assign the IP address: DHCP Server assigns the IP address without an expiration time limitation to the Clients. (3) Dynamically assign the IP address: DHCP Server assigns the IP address with an expiration time. When the time for the IP address expired, the Client should apply for a new one. 199