ZyXEL GS1510-24 User Guide - Page 105
ARP Inspection Overview
 |
View all ZyXEL GS1510-24 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 105 highlights
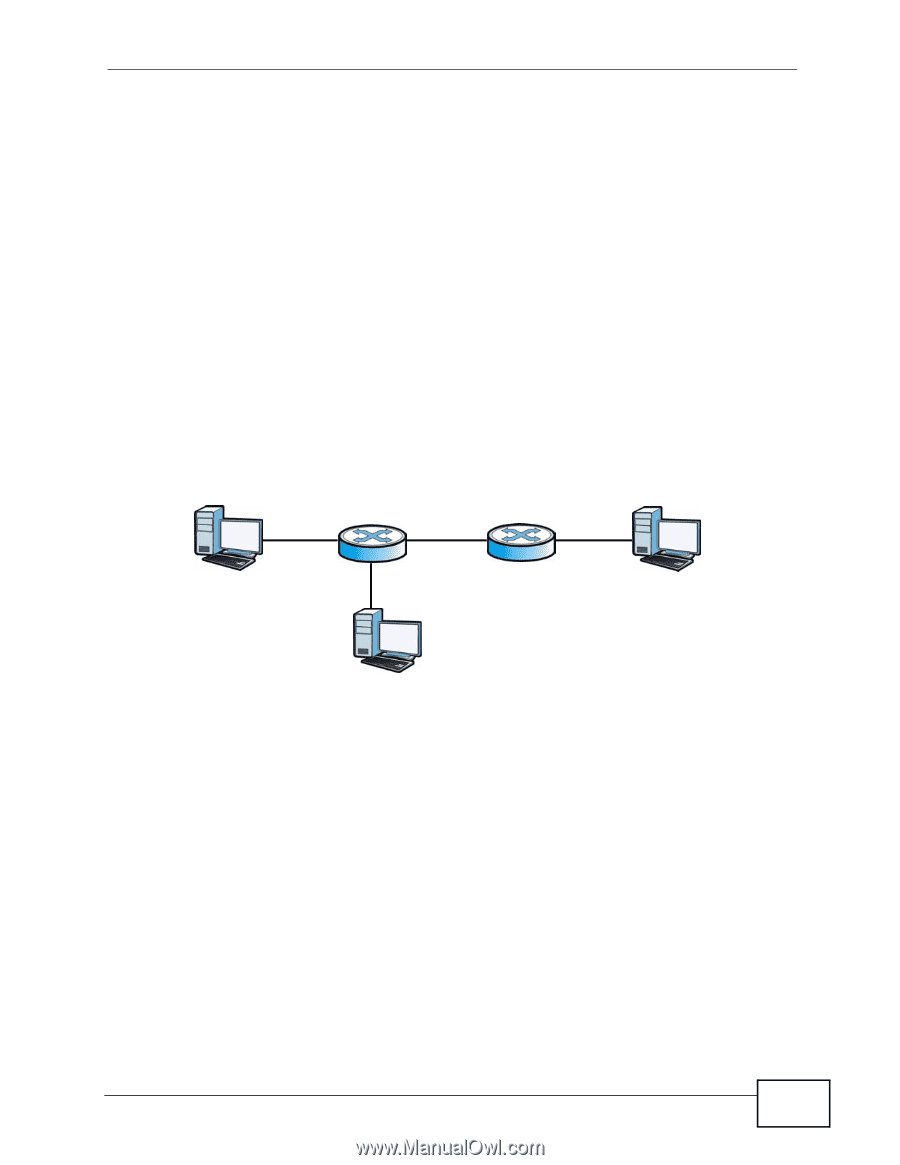
Chapter 18 IP Source Guard 18.3.1.3 Configuring DHCP Snooping Follow these steps to configure DHCP snooping on the Switch. 1 Enable DHCP snooping on the Switch. 2 Enable DHCP snooping on each VLAN. 3 Configure trusted and untrusted ports. 4 Configure static bindings. 18.3.2 ARP Inspection Overview Use ARP inspection to filter unauthorized ARP packets on the network. This can prevent many kinds of man-in-the-middle attacks, such as the one in the following example. Figure 54 Example: Man-in-the-middle Attack A B X In this example, computer B tries to establish a connection with computer A. Computer X is in the same broadcast domain as computer A and intercepts the ARP request for computer A. Then, computer X does the following things: • It pretends to be computer A and responds to computer B. • It pretends to be computer B and sends a message to computer A. As a result, all the communication between computer A and computer B passes through computer X. Computer X can read and alter the information passed between them. 18.3.2.1 ARP Inspection and MAC Address Filters When the Switch identifies an unauthorized ARP packet, it automatically creates a MAC address filter to block traffic from the source MAC address and source VLAN ID of the unauthorized ARP packet. You can configure how long the MAC address filter remains in the Switch. GS1510 Series User's Guide 105