ZyXEL GS1510-24 User Guide - Page 86
Port Priority
 |
View all ZyXEL GS1510-24 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 86 highlights
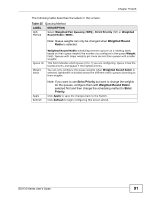
Chapter 15 QoS 15.3.1.1 Weighted Round Robin (WRR) Round Robin scheduling services queues on a rotating basis and is activated only when a port has more traffic than it can handle. A queue is given an amount of bandwidth irrespective of the incoming traffic on that port. This queue then moves to the back of the list. The next queue is given an equal amount of bandwidth, and then moves to the end of the list; and so on, depending on the number of queues being used. This works in a looping fashion until a queue is empty. Weighted Round Robin (WRR) scheduling uses the same algorithm as round robin scheduling, but services queues based on their priority and queue weight (the number you configure in the queue Weight field) rather than a fixed amount of bandwidth. WRR is activated only when a port has more traffic than it can handle. Queues with larger weights get more service than queues with smaller weights. This queuing mechanism is highly efficient in that it divides any available bandwidth across the different traffic queues and returns to queues that have not yet emptied. 15.3.2 QoS Enhancement You can configure the Switch to prioritize traffic even if the incoming packets are not marked with IEEE 802.1p priority tags or change the existing priority tags based on the criteria you select. The Switch allows you to choose one of the following methods for assigning priority to incoming packets on the Switch: Port Based QoS - Assign priority to packets based on the incoming port on the Switch. See Section 15.4 on page 86. DSCP Based QoS - Assign priority to packets based on their Differentiated Services Code Points (DSCPs). See Section 15.5.1 on page 88. Note: Advanced QoS methods only affect the internal priority queue mapping for the Switch. The Switch does not modify the IEEE 802.1p value for the egress frames. You can choose one of these ways to alter the way incoming packets are prioritized or you can choose not to use any QoS enhancement setting on the Switch. 15.4 Port Priority Use the Port Priority screen to specify IEEE 802.1p priority for each port. Packets without 802.1p priority tags will be applied the priority settings according to the 86 GS1510 Series User's Guide