ZyXEL GS1510-24 User Guide - Page 153
Table 50, Table 51
 |
View all ZyXEL GS1510-24 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 153 highlights
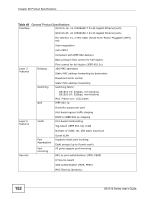
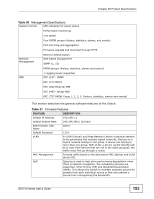
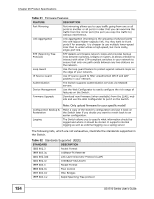
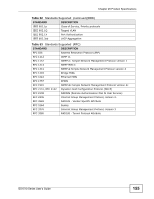
Chapter 25 Product Specifications Table 50 Management Specifications System Control LED indication for power status Performance monitoring Line speed Four RMON groups (history, statistics, alarms, and events) Port mirroring and aggregation Firmware upgrade and download through HTTP Network Management Reset to default button Web-based management SNMP v1, v2c RMON groups (history, statistics, alarms and events) 1 Logging server supported MIB RFC 1157 - SNMP RFC 1213 MIB II RFC 1643 Ethernet MIB RFC 1493 - Bridge MIB RFC 1757 RMON Group 1, 2, 3, 9 (history, statistics, alarms and events) This section describes the general software features of the Switch. Table 51 Firmware Features FEATURE DESCRIPTION Default IP Address 192.168.1.1 Default Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 (24 bits) Administrator User Name admin Default Password 1234 VLAN A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) allows a physical network to be partitioned into multiple logical networks. Devices on a logical network belong to one group. A device can belong to more than one group. With VLAN, a device cannot directly talk to or hear from devices that are not in the same group(s); the traffic must first go through a router. MAC Management Forward traffic based on the destination MAC address and VLAN group (ID). QoS Queuing is used to help solve performance degradation when there is network congestion. Two scheduling services are supported: Strict Priority (SP) and Weighted Round Robin (WRR). This allows the Switch to maintain separate queues for packets from each individual source or flow and prevent a source from monopolizing the bandwidth. GS1510 Series User's Guide 153