Compaq Evo n800c Hardware Guide, Compaq Notebook Series - Page 64
Understanding Drive Terms, Terms for Types of Drives, Terms for Drive Media - usb drivers
 |
View all Compaq Evo n800c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 64 highlights
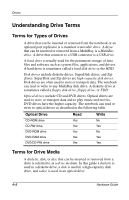
Drives Understanding Drive Terms Terms for Types of Drives A drive that can be inserted or removed from the notebook or an optional port replicator is a standard removable drive. A drive that can be inserted or removed from a MultiBay is a MultiBay drive. A drive that connects to a USB connector is a USB drive. A hard drive is usually used for the permanent storage of data files and software such as system files, applications, and drivers. A hard drive is sometimes called a hard disk drive or the HDD. Disk drives include diskette drives, SuperDisk drives, and Zip drives. SuperDisk and Zip drives are high-capacity disk drives. Disk drives are often used to store or transport data. The notebook can read or write to any MultiBay disk drive. A diskette drive is sometimes called a floppy disk drive, floppy drive, or FDD. Optical drives include CD and DVD drives. Optical drives are used to store or transport data and to play music and movies. DVD drives have the higher capacity. The notebook can read or write to optical drives as described in the following table. Optical Drive CD-ROM drive CD-RW drive DVD-ROM drive DVD-RAM drive DVD/CD-RW drive Read Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Write No Yes No Yes Yes Terms for Drive Media A diskette, disk, or disc that can be inserted or removed from a drive is referred to as a drive medium. In this guide a diskette is used in a diskette drive, a disk is used in a high-capacity disk drive, and a disc is used in an optical drive. 4-2 Hardware Guide