HP Rp2430 rp24xx A180 User Manual - Page 71
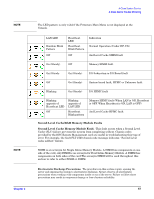
System Board Fault, High Priority Machine Check (HPMC), or Unknown Fault., I/O HPMC Fault.
 |
View all HP Rp2430 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 71 highlights
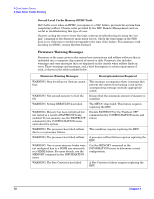
A-Class System Service A-Class Server Trouble Shooting Step 5. If the fault recurs, the I/O card in the bottom slot is the cause of the I/O Subsystem or I/O Board Fault. Replace that I/O board. Step 6. If the fault does not recur, install the second I/O card, power up the server, and observe the front panel LEDs. Step 7. If the problem recurs, replace the top I/O card. Step 8. If replacing the I/O card does not clear the I/O Subsystem or I/O Board Fault, the problem is with the system board. To change the system board, you must replace the A-Class Exchange Base Unit (EBU). Refer to the Replacing an A-Class Server Exchange Base Unit (EBU) section. System Board Fault, High Priority Machine Check (HPMC), or Unknown Fault. This fault occurs when the system board has an irrecoverable fault or an HPMC prevents the system from completing selftest. Chassis codes provided by the HSC Remote Management card are useful for troubleshooting this type of error, because HPMCs generate many chassis codes and some chassis codes indicate a specific fault. To troubleshoot I/O Subsystem or I/O Board Faults, power on the server and observe both the front panel LEDs and the console. If the server does not boot to the point where output displays on the console, the system board is the problem. To change the system board, you must replace the A-Class Exchange Base Unit (EBU). Refer to the Replacing an A-Class Server Exchange Base Unit (EBU) section. If power cycling the server clears the fault, continue troubleshooting by entering the "ser pim" command at the firmware main menu screen. Check the timestamp on the PIM data to see if the time recorded corresponds to the time of the failure. For assistance with decoding an HPMC, contact Hewlett-Packard. I/O HPMC Fault. I/O Subsystem or I/O Board faults occur when an HPMC, in response to an I/O failure, prevents the system from completing selftest. Chassis codes provided by the HSC Remote Management card are useful in troubleshooting this type of error, because HPMCs generate many chassis codes and some chassis codes indicate a specific fault. To troubleshoot an I/O HPMC fault, refer to the I/O Subsystem or I/O Board Fault section. If power cycling the server clears the fault, continue troubleshooting by using the "ser pim" command at the firmware main menu screen. Check the timestamp on the PIM data to see if the time recorded corresponds to the time of the failure. For assistance with decoding an HPMC, contact Hewlett-Packard. RAM HPMC Fault. RAM faults occur when an HPMC, in response to a RAM failure, prevents the system from completing selftest. Chassis codes provided by the HSC Remote Management card are useful in troubleshooting this type of error. To troubleshoot a RAM HPMC fault, refer to the Random Access Memory (RAM) Module Fault. section. If power cycling the server clears the fault, continue troubleshooting by using the "ser pim" command at the firmware main menu screen. Check the timestamp on the PIM data to see if the time recorded corresponds to the time of the failure. For assistance with decoding an HPMC, contact Hewlett-Packard. Chapter 3 71