Cisco NM-8B-U User Guide - Page 14
Timer, Purpose, STP Timers, Spanning Tree Port States
 |
UPC - 074632001001
View all Cisco NM-8B-U manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 14 highlights
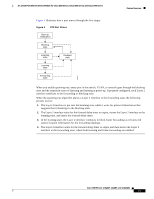
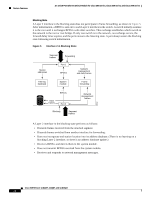
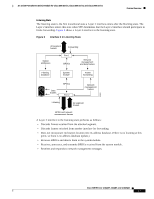
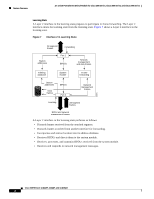
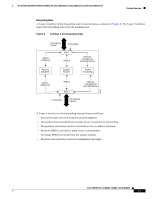
Feature Overview 16- and 36-Port Ethernet Switch Module for Cisco 2600 Series, Cisco 3600 Series, and Cisco 3700 Series STP Timers Table 2 describes the STP timers that affect the entire spanning tree performance: Table 2 STP Timers Timer Hello timer Forward delay timer Maximum age timer Purpose Determines how often the switch broadcasts hello messages to other switches. Determines how long each of the listening and learning states will last before the port begins forwarding Determines the amount of time protocol information received on a port is stored by the switch. Spanning Tree Port States Propagation delays can occur when protocol information passes through a switched LAN. As a result, topology changes can take place at different times and at different places in a switched network. When a Layer 2 interface changes directly from nonparticipation in the spanning tree topology to the forwarding state, it can create temporary data loops. Ports must wait for new topology information to propagate through the switched LAN before starting to forward frames. They must allow the frame lifetime to expire for frames that have been forwarded using the old topology. Each Layer 2 interface on a switch using spanning tree exists in one of the following five states: • Blocking-The Layer 2 interface does not participate in frame forwarding. • Listening-First transitional state after the blocking state when spanning tree determines that the Layer 2 interface should participate in frame forwarding. • Learning-The Layer 2 interface prepares to participate in frame forwarding. • Forwarding-The Layer 2 interface forwards frames. • Disabled-The Layer 2 interface does not participate in spanning tree and is not forwarding frames. A Layer 2 interface moves through these five states as follows: • From initialization to blocking • From blocking to listening or to disabled • From listening to learning or to disabled • From learning to forwarding or to disabled • From forwarding to disabled Cisco IOS Release 12.2(2)XT, 12.2(8)T, and 12.2(15)ZJ 14