Dell PowerEdge R760XA Installation and Service Manual - Page 42
SATA Settings, NVMe Settings, Boot Settings, Table 39. SATA Settings details
 |
View all Dell PowerEdge R760XA manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 42 highlights
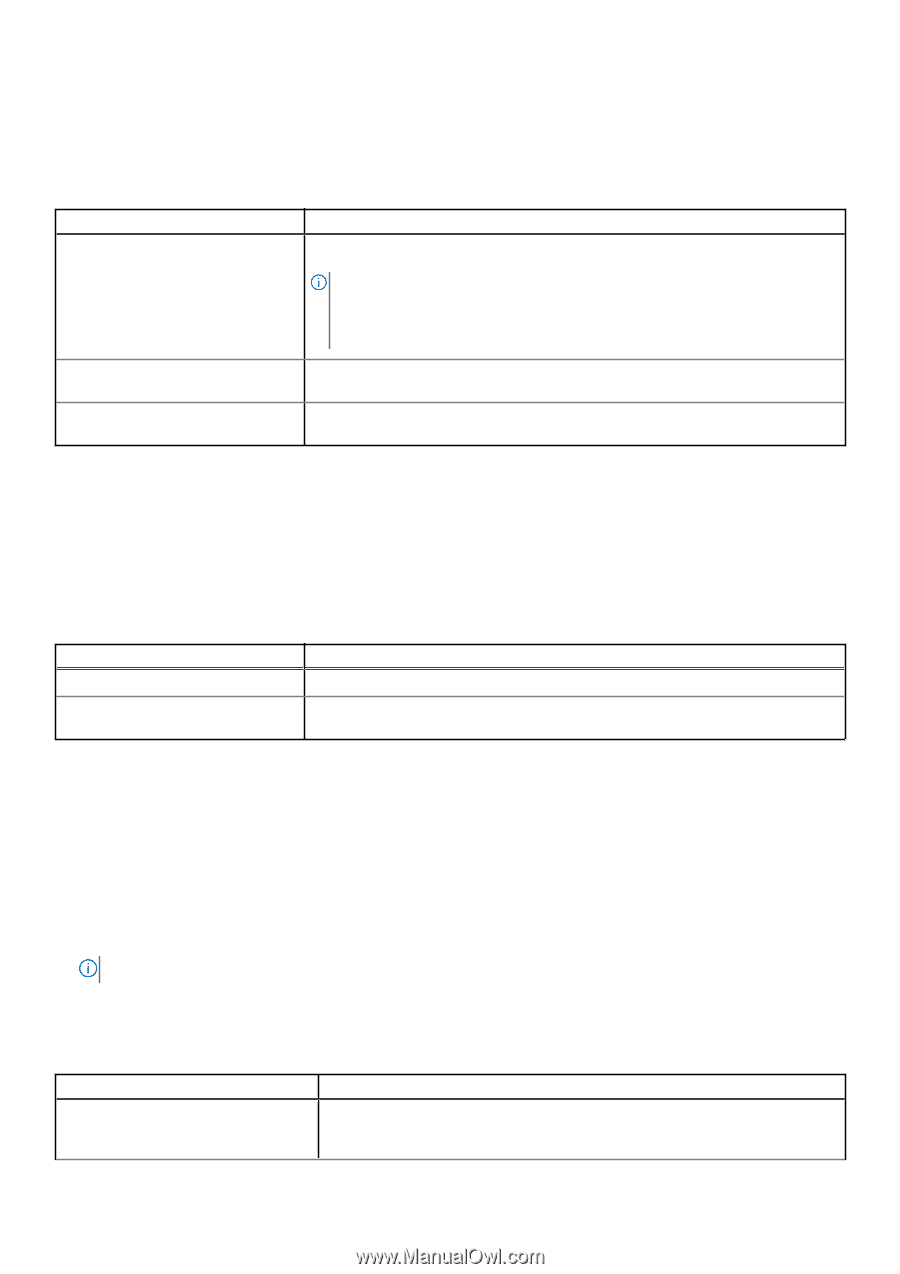
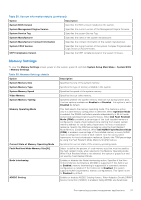
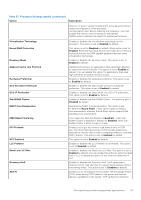
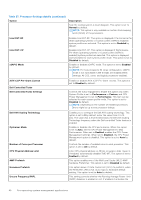
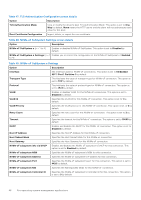
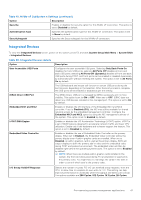
SATA Settings To view the SATA Settings screen, power on the system, press F2, and click System Setup Main Menu > System BIOS > SATA Settings. Table 39. SATA Settings details Option Embedded SATA Description Enables the embedded SATA option to be set to Off, AHCI mode , or RAID mode. This option is set to AHCI Mode by default. NOTE: 1. You might also need to change the Boot Mode setting to UEFI. Otherwise, you should set the field to Non-RAID mode. 2. No ESXi and Ubuntu OS support under RAID mode. Security Freeze Lock Write Cache Sends Security Freeze Lock command to the embedded SATA drives during POST. This option is applicable only for AHCI Mode. This option is set to Enabled by default. Enables or disables the command for the embedded SATA drives during POST. This option is applicable only for AHCI Mode. This option is set to Disabled by default. NVMe Settings This option sets the NVMe drive mode. If the system contains NVMe drives that you want to configure in a RAID array, you must set both this field and the Embedded SATA field on the SATA settings menu to RAID Mode. You may also need to change the Boot Mode setting to UEFI. To view the NVMe Settings screen, power on the system, press F2, and click System Setup Main Menu > System BIOS > NVMe Settings. Table 40. NVMe Settings details Option NVMe mode Description Enables or disables the boot mode. The option is set to Non-RAID mode by default. BIOS NVMe Driver Sets the drive type to boot the NVMe driver. The available options are Dell Qualified Drives and All Drives. This option is set to Dell Qualified Drives by default. Boot Settings You can use the Boot Settings screen to set the boot mode to either BIOS or UEFI. It also enables you to specify the boot order. The Boot Settings only support UEFI mode. ● UEFI: The Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is a new interface between operating systems and platform firmware. The interface consists of data tables with platform related information, boot and runtime service calls that are available to the operating system and its loader. The following benefits are available when the Boot Mode is set to UEFI: ○ Support for drive partitions larger than 2 TB. ○ Enhanced security (e.g., UEFI Secure Boot). ○ Faster boot time. NOTE: You must use only the UEFI boot mode in order to boot from NVMe drives. ● BIOS: The BIOS Boot Mode is the legacy boot mode. It is maintained for backward compatibility. To view the Boot Settings screen, power on the system, press F2, and click System Setup Main Menu > System BIOS > Boot Settings. Table 41. Boot Settings details Option Boot Mode Description Enables you to set the boot mode of the system. If the operating system supports UEFI, you can set this option to UEFI. Setting this field to BIOS allows compatibility with non-UEFI operating systems. This option is set to UEFI by default. 42 Pre-operating system management applications