HP 6120XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches Advanced Traffic Management G - Page 180
Honor New Priority, Set Priority, Set Policy
 |
View all HP 6120XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 180 highlights
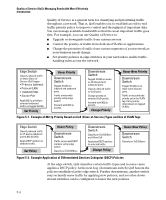
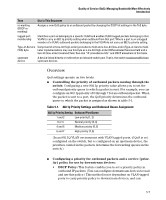
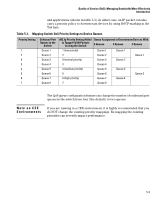
Quality of Service (QoS): Managing Bandwidth More Effectively Introduction Quality of Service is a general term for classifying and prioritizing traffic throughout a network. That is, QoS enables you to establish an end-to-end traffic priority policy to improve control and throughput of important data. You can manage available bandwidth so that the most important traffic goes first. For example, you can use Quality of Service to: ■ Upgrade or downgrade traffic from various servers. ■ Control the priority of traffic from dedicated VLANs or applications. ■ Change the priorities of traffic from various segments of your network as your business needs change. ■ Set priority policies in edge switches in your network to enable traffic- handling rules across the network. Edge Switch Classify inbound traffic on these Class-ofService (CoS) types: • IP-device (address) • Protocol (LAN) • VLAN-ID (VID). • Source-Port Apply 802.1p priority to selected outbound traffic on tagged VLANs. Set Priority Honor Priority Downstream Switch Tagged VLANs on inbound and outbound ports. Traffic arrives with priority set by edge switch Forward with 802.1p priority. Downstream Switch Tagged VLANs on some or all inbound and outbound ports. Classify inbound traffic on CoS types. Change priority on selected CoS type(s). Forward with 802.1p priority. Change Priority Honor New Priority Downstream Switch Tagged VLANs on at least some inbound ports. Traffic arrives with the priority set in the VLAN tag. Carry priority downstream on tagged VLANs. Figure 5-1. Example of 802.1p Priority Based on CoS (Class-of-Service) Types and Use of VLAN Tags Edge Switch Classify inbound traffic on IP-device (address) and VLAN-ID (VID). Apply DSCP markers to selected traffic. Set Policy Honor Policy Downstream Switch Traffic arrives with DSCP markers set by edge switch Classify on ToS DiffServ. Downstream Switch Classify on ToS DiffServ and Other CoS Apply new DSCP markers to selected traffic. Change Policy Honor New Policy Downstream Switch Classify on ToS Diffserv Figure 5-2. Example Application of Differentiated Services Codepoint (DSCP) Policies At the edge switch, QoS classifies certain traffic types and in some cases applies a DSCP policy. At the next hop (downstream switch) QoS honors the policies established at the edge switch. Further downstream, another switch may reclassify some traffic by applying new policies, and yet other downstream switches can be configured to honor the new policies. 5-4