HP 6120XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches Advanced Traffic Management G - Page 246
Applying a Traffic Template, Example of Valid Traffic Template with Remapped Queue
 |
View all HP 6120XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 246 highlights
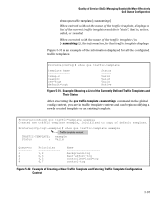
Quality of Service (QoS): Managing Bandwidth More Effectively QoS Queue Configuration ProCurve(cfg-tcgt-example)# map-traffic-group 2 priority 0 ProCurve(cfg-tcgt-example)# show qos traffic-template example TRAFFIC-TEMPLATE: example Status : Valid -------1 2 3 4 ------------1,2 3,0 4,5 6,7 background-tcg best-effort-tcg controlled-load-tcg control-tcg Figure 5-35. Example of Valid Traffic Template with Remapped Queue After modifying a traffic template, you must apply it to the switch to activate the new mapping. See "Applying a Traffic Template", below. Applying a Traffic Template After creating a traffic template with the desired options, you must apply it to the module or switch (in the global config context). Traffic templates must be applied to the entire switch, so enter all or the entire range of ports. Syntax: interface policy traffic-template Applies the specified traffic template to the module or switch and forces a write memory and reboot. All ports in the module or switch (1-N) must be specified, or just enter the parameter "all". ProCurve(config)# int all ProCurve(eth-1-24)# policy traffic-template example This command will modify the current running configuration, will execute 'write memory' to replace the startup configuration, then reboot. Continue? [y/n] y The traffic template named "example" is applied to all the ports in the module or switch. Figure 5-36. Example of Applying a Traffic Template to a Switch Traffic templates can only be applied by rebooting the switch. If you enter "n", the traffic template is not applied. 5-70