HP 6120XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches Advanced Traffic Management G - Page 188
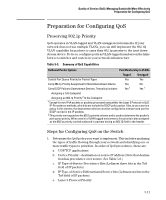
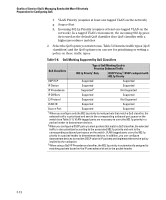
Table 5-6., QoS Marking Supported by QoS Classifiers
 |
View all HP 6120XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 188 highlights
Quality of Service (QoS): Managing Bandwidth More Effectively Preparation for Configuring QoS f. VLAN Priority (requires at least one tagged VLAN on the network) g. Source-Port h. Incoming 802.1p Priority (requires at least one tagged VLAN on the network). In a tagged VLAN environment, the incoming 802.1p priority is used as the default QoS classifier if no QoS classifier with a higher precedence matches 2. Select the QoS option you want to use. Table 5-6 lists the traffic types (QoS classifiers) and the QoS options you can use for prioritizing or setting a policy on these traffic types: Table 5-6. QoS Marking Supported by QoS Classifiers QoS Classifiers Type of QoS Marking Used to Prioritize Outbound Traffic 802.1p Priority1 Only DSCP Policy2: DSCP codepoint with 802.1p Priority UDP/TCP Supported Supported IP Device IP Precedence Supported Supported3 Supported Not Supported IP DiffServ Supported Supported L3 Protocol Supported Not Supported VLAN ID Supported Supported Source Port Supported Supported 1 When you configure only the 802.1p priority to mark packets that match a QoS classifier, the selected traffic is prioritized and sent to the corresponding outbound port queue on the switch (see Table 5-1). VLAN-tagged ports are necessary to carry the 802.1p priority in a packet header to downstream devices. 2 When you configure a DSCP policy to mark packets that match a QoS classifier, the selected traffic is also prioritized according to the associated 802.1p priority and sent to the corresponding outbound port queue on the switch. VLAN-tagged ports carry the 802.1p priority in a packet header to downstream devices. In addition, you can configure downstream devices to read the DSCP value in IP packets and implement the service policy implied by the codepoint. 3 When using a QoS IP Precedence classifier, the 802.1p priority is automatically assigned to matching packets based on the IP precedence bit set in the packet header. 5-12