HP 6120XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches Advanced Traffic Management G - Page 204
Assigning an 802.1p Priority to IPv4 Packets on the Basis of Incoming DSCP,
 |
View all HP 6120XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 204 highlights
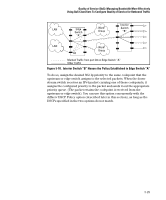
Quality of Service (QoS): Managing Bandwidth More Effectively Using QoS Classifiers To Configure Quality of Service for Outbound Traffic show qos type-of-service When ip-precedence is enabled (or if neither ToS option is configured), shows the ToS configuration status. If diffservices is enabled, lists codepoint data as described under "Assigning a DSCP Policy on the Basis of the DSCP in IPv4 Packets Received from Upstream Devices" on page 5-33. With this option, prioritization of outbound packets relies on the IP-Precedence bit setting that IP packets carry with them from upstream devices and applications. To configure and verify this option: Default ToS Configuration Current ToS Configuration Figure 5-9. Example of Enabling ToS IP-Precedence Prioritization To replace this option with the ToS diff-services option, just configure diffservices as described below, which automatically disables IP-Precedence. To disable IP-Precedence without enabling the diff-services option, use this command: ProCurve(config)# no qos type-of-service Assigning an 802.1p Priority to IPv4 Packets on the Basis of Incoming DSCP One of the best uses for this option is on an interior switch where you want to honor (continue) a policy set on an edge switch. That is, it enables you to select incoming packets having a specific DSCP and forward these packets with the desired 802.1p priority. For example, if an edge switch "A" marks all packets received on port A5 with a particular DSCP, you can configure a downstream (interior) switch "B" to handle such packets with the desired priority (regardless of whether 802.1Q tagged VLANs are in use). 5-28