HP 6120XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches Advanced Traffic Management G - Page 30
Introduction, General VLAN Operation
 |
View all HP 6120XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 30 highlights
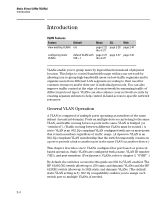
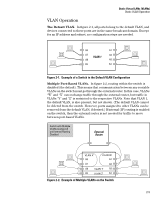
Static Virtual LANs (VLANs) Introduction Introduction VLAN Features Feature Default Menu CLI Web view existing VLANs n/a page 2-22 page 2-28 page 2-41 thru 2-27 configuring static VLANs default VLAN with page 2-22 page 2-27 page 2-41 VID = 1 thru 2-27 VLANs enable you to group users by logical function instead of physical location. This helps to control bandwidth usage within your network by allowing you to group high-bandwidth users on low-traffic segments and to organize users from different LAN segments according to their need for common resources and/or their use of individual protocols. You can also improve traffic control at the edge of your network by separating traffic of different protocol types. VLANs can also enhance your network security by creating separate subnets to help control in-band access to specific network resources. General VLAN Operation A VLAN is comprised of multiple ports operating as members of the same subnet (broadcast domain). Ports on multiple devices can belong to the same VLAN, and traffic moving between ports in the same VLAN is bridged (or "switched"). (Traffic moving between different VLANs must be routed.) A static VLAN is an 802.1Q-compliant VLAN configured with one or more ports that remain members regardless of traffic usage. (A dynamic VLAN is an 802.1Q-compliant VLAN membership that the switch temporarily creates on a port to provide a link to another port in the same VLAN on another device.) This chapter describes static VLANs configured for port-based or protocolbased operation. Static VLANs are configured with a name, VLAN ID number (VID), and port members. (For dynamic VLANs, refer to chapter 3, "GVRP" .) By default, the switches covered in this guide are 802.1Q VLAN-enabled. The HP 6120G/XG switch allows up to 256 static and dynamic VLANs and the HP 6120XG switch allows up to 1024 static and dynamic VLANs. (The default static VLAN setting is 8). 802.1Q compatibility enables you to assign each switch port to multiple VLANs, if needed. 2-4