HP 6120XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches Advanced Traffic Management G - Page 183
Overview, DSCP Policy
 |
View all HP 6120XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 183 highlights
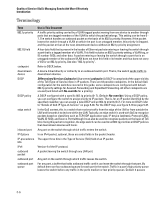
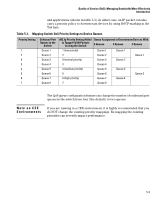
Quality of Service (QoS): Managing Bandwidth More Effectively Introduction Term Use in This Document re-marking (DSCP remarking) Assigns a new QoS policy to an outbound packet by changing the DSCP bit settings in the ToS byte. tagged port membership Identifies a port as belonging to a specific VLAN and enables VLAN-tagged packets belonging to that VLAN to carry an 802.1p priority setting when outbound from that port. Where a port is an untagged member of a VLAN, outbound packets belonging to that VLAN do not carry an 802.1p priority setting. Type-of-Service Comprised of a three-bit (high-order) precedence field and a five-bit (low-order) Type-of-Service field. (ToS) byte Later implementations may use this byte as a six-bit (high-order) Differentiated Services field and a two-bit (low-order) reserved field. See also "IP-precedence bits" and DSCP elsewhere in this table. upstream device A device linked directly or indirectly to an inbound switch port. That is, the switch receives traffic from upstream devices. Overview QoS settings operate on two levels: ■ Controlling the priority of outbound packets moving through the switch: Configuring a new 802.1p priority value allows you to set the outbound priority queue to which a packet is sent. For example, you can configure an 802.1p priority of 0 through 7 for an outbound packet. When the packet is sent to a port, the QoS priority determines the outbound queue to which the packet is assigned as shown in table 5-1. Table 5-1. 802.1p Priority Settings and Outbound Queue Assignment 802.1p Priority Setting Outbound Port Queue 1 and 2 Low priority (1, 2) 0 or 3 Normal priority (3, 4) 4 and 5 Medium priority (5, 6) 6 and 7 High priority (7, 8) (In an 802.1Q VLAN environment with VLAN-tagged ports, if QoS is not configured on the switch, but is configured on an upstream device, the priorities carried in the packets determine the forwarding queues in the switch.) ■ Configuring a priority for outbound packets and a service (priority) policy for use by downstream devices: • DSCP Policy: This feature enables you to set a priority policy in outbound IP packets. (You can configure downstream devices to read and use this policy.) This method is not dependent on VLAN-tagged ports to carry priority policy to downstream devices, and can: 5-7