HP GbE2c HP GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for c-Class BladeSystem ISCLI Referenc - Page 105
Spanning Tree port configuration, spanning-tree stp, bridge priority, bridge hello-time
 |
UPC - 808736802215
View all HP GbE2c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 105 highlights
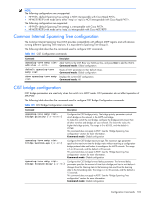
The following table describes the Bridge Spanning Tree Configuration commands. Table 108 Bridge Spanning Tree Configuration commands Command spanning-tree stp {} bridge priority {} spanning-tree stp {} bridge hello-time {} spanning-tree stp {} bridge maximum-age {} spanning-tree stp {} bridge forward-delay {} show spanning-tree stp {} bridge Description Configures the bridge priority. The bridge priority parameter controls which bridge on the network is the STP root bridge. To make this switch the root bridge, configure the bridge priority lower than all other switches and bridges on your network. The lower the value, the higher the bridge priority. The range is 0 to 65535, and the default is 32768. RSTP/MSTP: The range is 0 to 61440, in steps of 4096 (0, 4096, 8192...), and the default is 32768. This command does not apply to MSTP. See the "Common Internal Spanning Tree configuration" section for more information. Command mode: Global configuration Configures the bridge hello time. The hello time specifies how often the root bridge transmits a configuration bridge protocol data unit (BPDU). Any bridge that is not the root bridge uses the root bridge hello value. The range is 1 to 10 seconds, and the default is 2 seconds. This command does not apply to MSTP. See the "Common Internal Spanning Tree configuration" section for more information. Command mode: Global configuration Configures the bridge maximum age. The maximum age parameter specifies the maximum time the bridge waits without receiving a configuration bridge protocol data unit before it reconfigures the STP network. The range is 6 to 40 seconds, and the default is 20 seconds. This command does not apply to MSTP. See the "Common Internal Spanning Tree configuration" section for more information. Command mode: Global configuration Configures the bridge forward delay parameter. The forward delay parameter specifies the amount of time that a bridge port has to wait before it changes from the listening state to the learning state and from the learning state to the forwarding state. The range is 4 to 30 seconds, and the default is 15 seconds. This command does not apply to MSTP. See the "Common Internal Spanning Tree configuration" section for more information. Command mode: Global configuration Displays the current bridge STP parameters. Command mode: All When configuring STP bridge parameters, the following formulas must be used: • 2*(fwd-1) > mxage • 2*(hello+1) < mxage Spanning Tree port configuration By default for STP/PVST+, Spanning tree is turned Off for downlink ports (1-16), and turned On for cross-connect ports (17-18), and uplink ports (20-24). By default for RSTP/MSTP, Spanning tree is turned On for all downlink ports (1-16), all cross-connect ports (17-18), and all uplink ports (20-24), with downlink ports configured as Edge ports. Spanning tree port parameters are used to modify STP operation on an individual port basis. STP port parameters include: • Port priority • Port path cost Configuration Commands 105