HP GbE2c HP GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for c-Class BladeSystem ISCLI Referenc - Page 46
IGMP multicast router port information, VRRP information
 |
UPC - 808736802215
View all HP GbE2c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 46 highlights
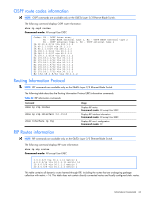
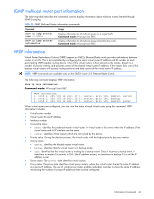
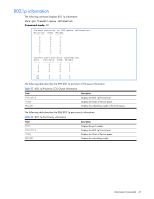
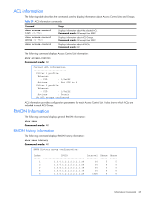
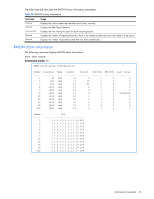
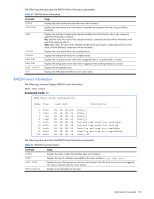
IGMP multicast router port information The following table describes the commands used to display information about multicast routers learned through IGMP Snooping. Table 36 IGMP Multicast Router information commands Command Usage show ip igmp mrouter vlan show ip igmp mrouter information Displays information for all multicast groups on a single VLAN. Command mode: All except User EXEC Displays information for all multicast groups learned by the switch. Command mode: All except User EXEC VRRP information Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) support on GbE2c Ethernet Blade switch provides redundancy between routers in a LAN. This is accomplished by configuring the same virtual router IP address and ID number on each participating VRRP-capable routing device. One of the virtual routers is then elected as the master, based on a number of priority criteria, and assumes control of the shared virtual router IP address. If the master fails, one of the backup virtual routers will assume routing authority and take control of the virtual router IP address. NOTE: VRRP commands are available only on the GbE2c Layer 2/3 Ethernet Blade Switch. The following command displays VRRP information: show ip vrrp information Command mode: All except User EXEC VRRP information: 1: vrid 2, 205.178.18.210, if 1, renter, prio 100, master, server 2: vrid 1, 205.178.18.202, if 1, renter, prio 100, backup 3: vrid 3, 205.178.18.204, if 1, renter, prio 100, master, proxy When virtual routers are configured, you can view the status of each virtual router using this command. VRRP information includes: • Virtual router number • Virtual router ID and IP address • Interface number • Ownership status • owner identifies the preferred master virtual router. A virtual router is the owner when the IP address of the virtual router and its IP interface are the same. • renter identifies virtual routers which are not owned by this device • Priority value. During the election process, the virtual router with the highest priority becomes master. • Activity status • master identifies the elected master virtual router. • backup identifies that the virtual router is in backup mode. • init identifies that the virtual router is waiting for a startup event. Once it receives a startup event, it transitions to master if its priority is 255, (the IP address owner), or transitions to backup if it is not the IP address owner. • Server status. The server state identifies virtual routers. • Proxy status. The proxy state identifies virtual proxy routers, where the virtual router shares the same IP address as a proxy IP address. The use of virtual proxy routers enables redundant switches to share the same IP address, minimizing the number of unique IP addresses that must be configured. Information Commands 46