HP GbE2c HP GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for c-Class BladeSystem ISCLI Referenc - Page 32
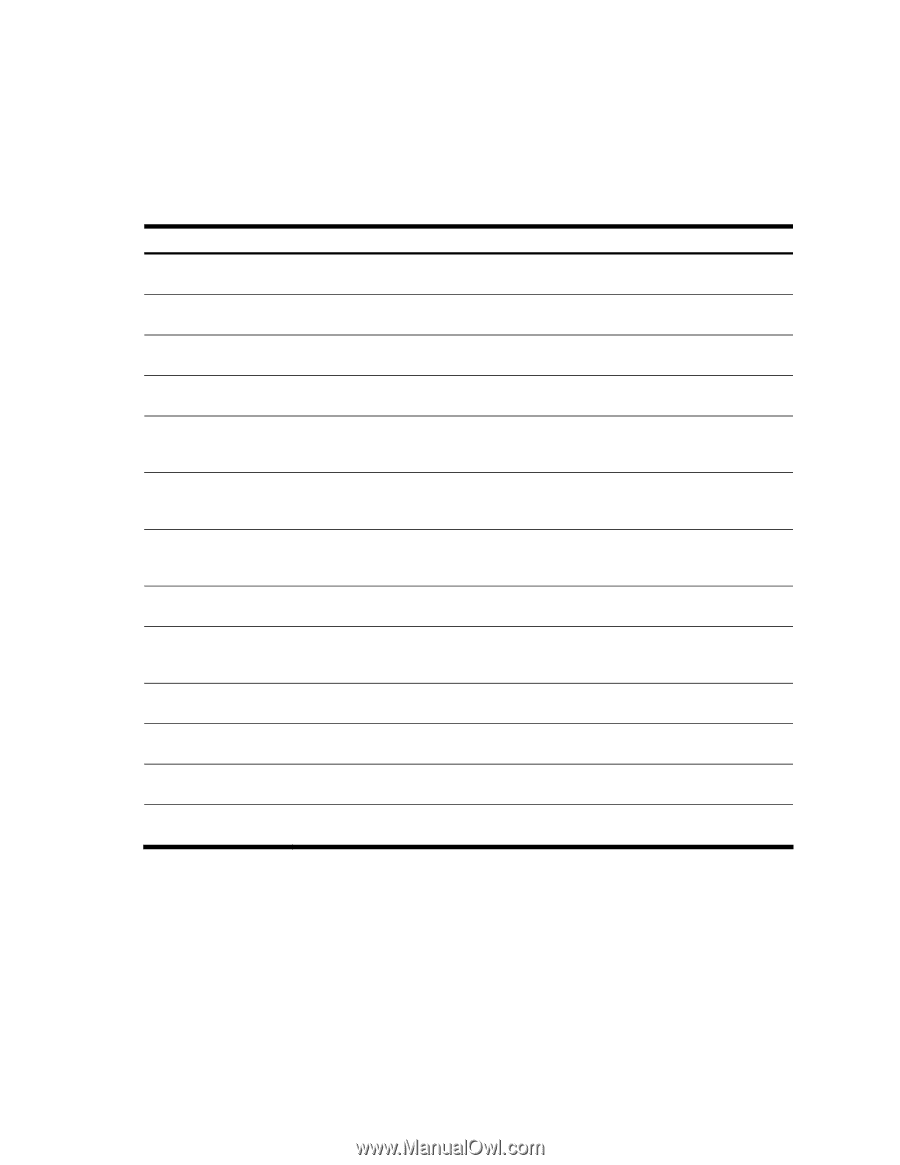
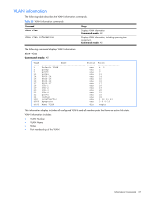
Current Root, Path-Cost, Priority bridge, Hello, MaxAge, FwdDel, Aging, Priority port, State
 |
UPC - 808736802215
View all HP GbE2c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 32 highlights
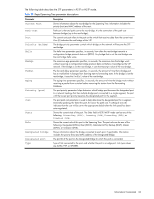
• Port number and priority • Cost • State • Port Fast Forwarding state • Designated bridge • Designated port The following table describes the STP parameters. Table 22 STP parameters Parameter Description Current Root Shows information about the root bridge for the Spanning Tree. Information includes the priority (hex) and MAC address of the root. Path-Cost Path-cost is the total path cost to the root bridge. It is the summation of the path cost between bridges (up to the root bridge). Port The current root port refers to the port on the switch that receives data from the current root. Zero (0) indicates the root bridge of the STP. Priority (bridge) The bridge priority parameter controls which bridge on the network will become the STP root bridge. Hello The hello time parameter specifies, in seconds, how often the root bridge transmits a configuration bridge protocol data unit (BPDU). Any bridge that is not the root bridge uses the root bridge hello value. MaxAge The maximum age parameter specifies, in seconds, the maximum time the bridge waits without receiving a configuration bridge protocol data unit before it reconfigures the STP network. If the bridge is not the root bridge, it uses the MaxAge value of the root bridge. FwdDel The forward delay parameter specifies, in seconds, the amount of time that a bridge port has to wait before it changes from learning state to forwarding state. If the bridge is not the root bridge, it uses the FwdDel value of the root bridge. Aging The aging time parameter specifies, in seconds, the amount of time the bridge waits without receiving a packet from a station before removing the station from the Forwarding Database. Priority (port) The port priority parameter helps determine which bridge port becomes the designated port. In a network topology that has multiple bridge ports connected to a single segment, the port with the lowest port priority becomes the designated port for the segment. Cost The port path cost parameter is used to help determine the designated port for a segment. Generally speaking, the faster the port, the lower the path cost. State The State field shows the current state of the port. The State field can be one of the following: BLOCKING, LISTENING, LEARNING, FORWARDING, or DISABLED. Designated bridge Shows information about the bridge connected to each port, if applicable. Information includes the priority (hex) and MAC address of the Designated Bridge. Designated port The port ID of the port on the Designated Bridge to which this port is connected. This information includes the port priority (hex) and the port number (hex). Information Commands 32