Dell Inspiron 15R 5521 Me and My Dell - Page 100
Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
 |
View all Dell Inspiron 15R 5521 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 100 highlights
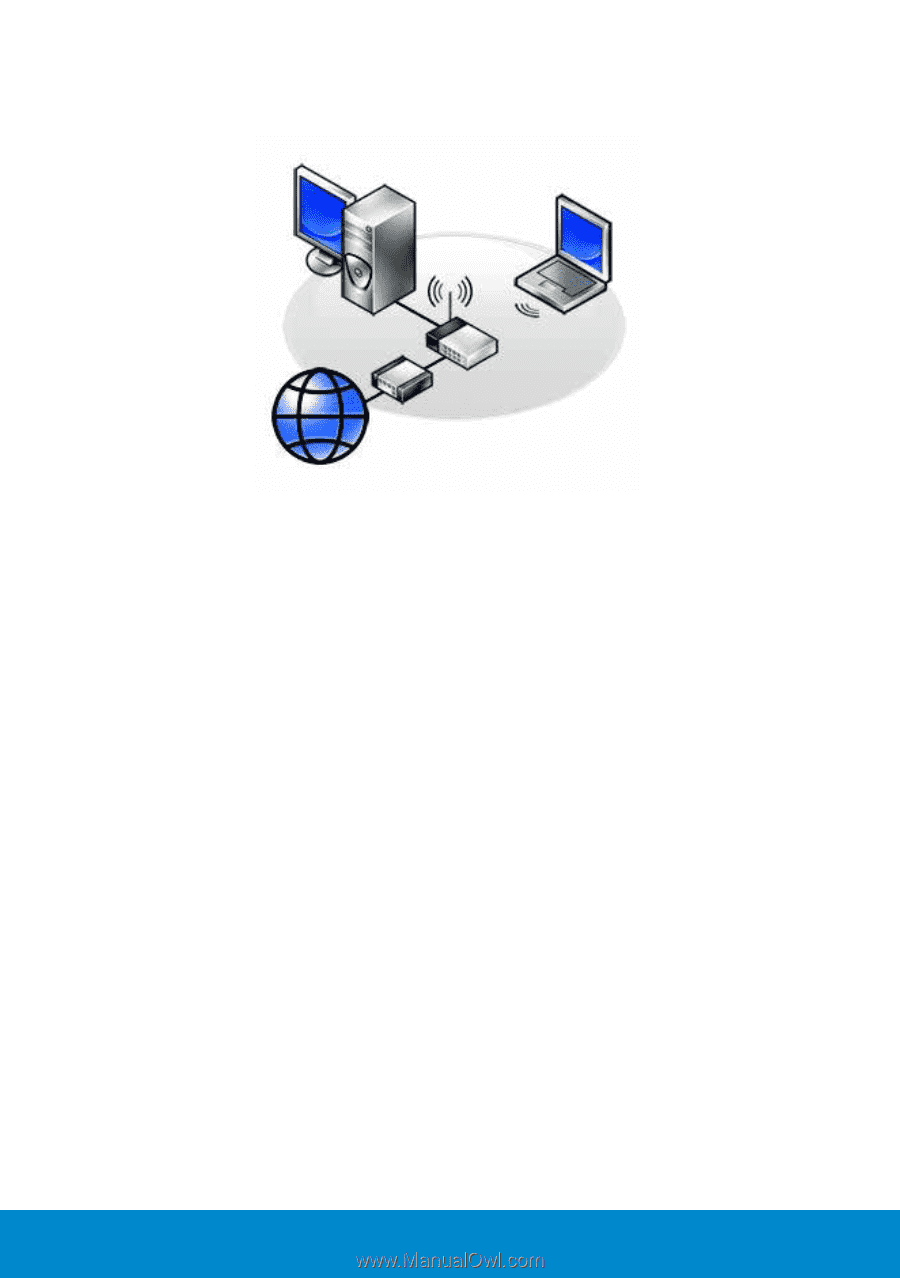
Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) WLAN connects two or more computers with each other and the Internet over the air waves rather than through a network cable connected to each computer. In a WLAN, a radio communications device (an access point or wireless router) connects the networked computers and peripherals, and provides Internet or network access. The access point or wireless router and the wireless network card in the computer communicate by broadcasting data from their antennas over the air waves. Wireless Wide Area Network (WWAN) WWAN is also known as Mobile Broadband network, is a high-speed digital cellular network that provides Internet access over a much wider geographical area than a WLAN, which typically covers only from 100 to 1000 feet. Your computer can maintain Mobile Broadband network access as long as the computer is within a cellular-data coverage zone. Contact your cellular/Internet service provider for coverage details. Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN) WPAN helps interconnect wireless devices centered around your personal workspace. WPAN technology supports communication over a short distance. Bluetooth, used as the basis for a new standard, IEEE 802.15. is an example of WPAN 100 Network