Nikon D100 Product Manual - Page 155
Shooting Options
 |
UPC - 018208252718
View all Nikon D100 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 155 highlights
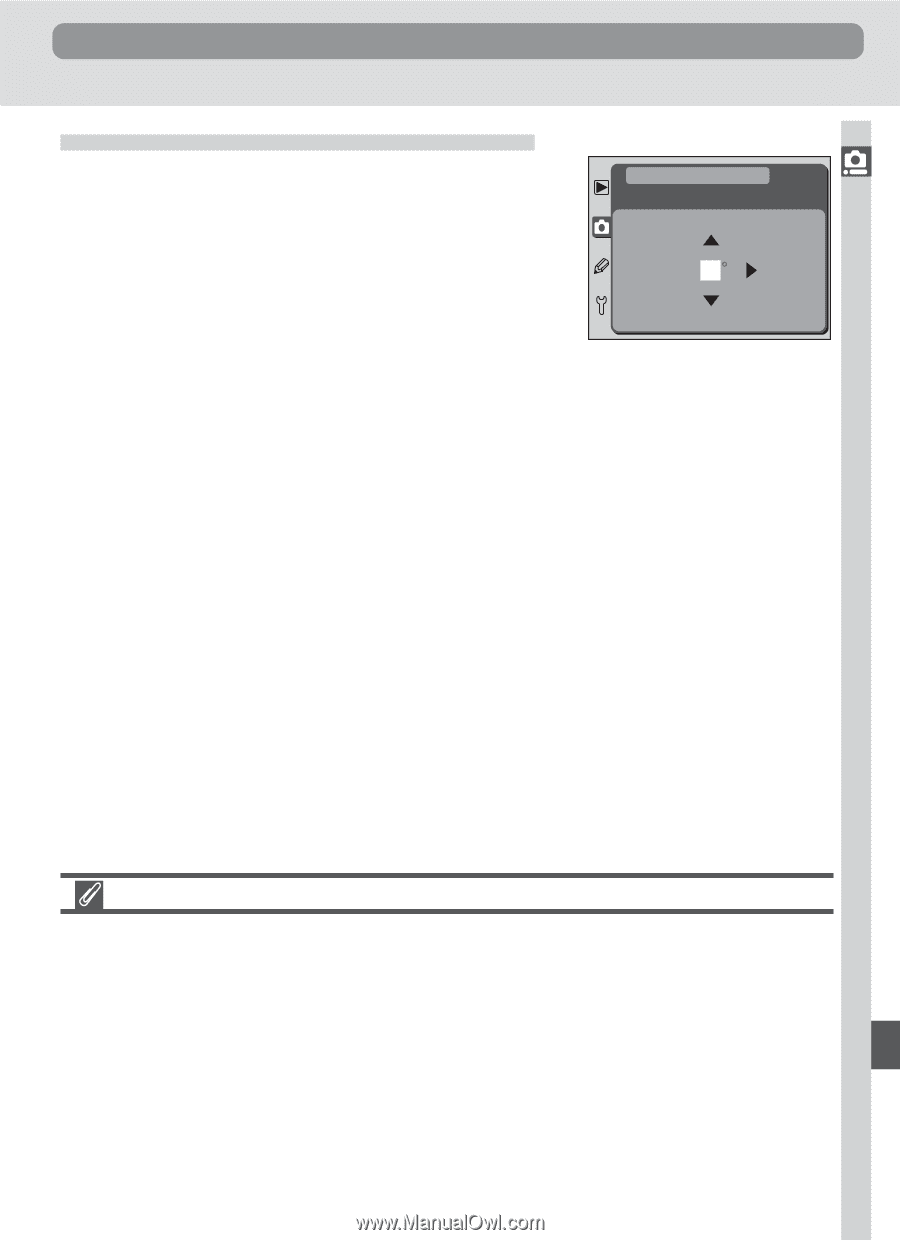
Menu Guide-The Shooting Menu Shooting Options Controlling Color: Hue Adjustment This option is used to adjust the hue of photo- graphs as they are taken. Hue can be adjusted in the range -9 ° to 9 ° in increments of 3 °. If red is taken as the starting color, raising hue above 0 ° (the default setting) would introduce a yellow cast, making colors that would be red at a setting of 0 ° appear increasingly orange. Lowering hue below 0 ° would introduce a blue cast, making colors that would be red at a setting of 0 ° appear increasingly purple. SHOOTING MENU Hue Adjustment 0 OK Hue The RGB color model used in digital photographs reproduces colors using differing amounts of red, green, and blue light. By mixing two colors of light, a variety of different colors can be produced. For example, red combined with a small amount of green light produces orange. If red and green are mixed in equal amounts, yellow results, while a smaller amount of red produces a yellow green. Mixing different amounts of red and blue light produces colors ranging from a reddish purple through purple to navy, while mixing different amounts of green and blue light produces colors ranging from emerald to turquoise. (Adding a third color of light results in lighter hues; if all three mixed in equal amounts, the results range from white through gray.) When this progression of hues is arranged in a circle, the result is known as a color wheel. 143