Cisco NME-16ES-1G User Guide - Page 15
STP Port States, learning state, and resets the forward delay timer. - how to configure
 |
UPC - 882658036101
View all Cisco NME-16ES-1G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 15 highlights
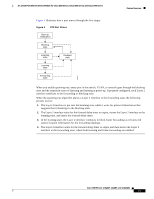
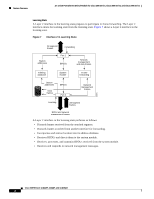
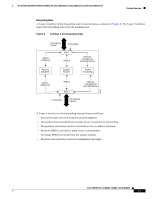
16- and 36-Port Ethernet Switch Module for Cisco 2600 Series, Cisco 3600 Series, and Cisco 3700 Series Feature Overview Figure 4 illustrates how a port moves through the five stages. Figure 4 STP Port States Boot-up initialization Blocking state Listening state Disabled state Learning state Forwarding state S5691 When you enable spanning tree, every port in the switch, VLAN, or network goes through the blocking state and the transitory states of listening and learning at power up. If properly configured, each Layer 2 interface stabilizes to the forwarding or blocking state. When the spanning tree algorithm places a Layer 2 interface in the forwarding state, the following process occurs: 1. The Layer 2 interface is put into the listening state while it waits for protocol information that suggests that it should go to the blocking state. 2. The Layer 2 interface waits for the forward delay timer to expire, moves the Layer 2 interface to the learning state, and resets the forward delay timer. 3. In the learning state, the Layer 2 interface continues to block frame forwarding as it learns end station location information for the forwarding database. 4. The Layer 2 interface waits for the forward delay timer to expire and then moves the Layer 2 interface to the forwarding state, where both learning and frame forwarding are enabled. Cisco IOS Release 12.2(2)XT, 12.2(8)T, and 12.2(15)ZJ 15