Cisco NME-16ES-1G User Guide - Page 23
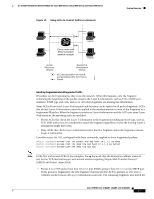
BackboneFast Example After Indirect Link Failure
 |
UPC - 882658036101
View all Cisco NME-16ES-1G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 23 highlights
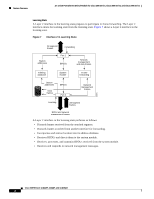
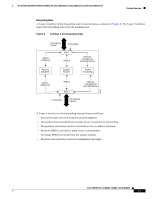
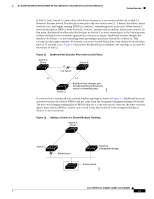
16- and 36-Port Ethernet Switch Module for Cisco 2600 Series, Cisco 3600 Series, and Cisco 3700 Series Feature Overview If link L1 fails, Switch C cannot detect this failure because it is not connected directly to link L1. However, because Switch B is directly connected to the root switch over L1, it detects the failure, elects itself the root, and begins sending BPDUs to Switch C, identifying itself as the root. When Switch C receives the inferior BPDUs from Switch B, Switch C assumes that an indirect failure has occurred. At that point, BackboneFast allows the blocked port on Switch C to move immediately to the listening state without waiting for the maximum aging time for the port to expire. BackboneFast then changes the interface on Switch C to the forwarding state, providing a path from Switch B to Switch A. This switchover takes approximately 30 seconds, twice the Forward Delay time if the default Forward Delay time of 15 seconds is set. Figure 11 shows how BackboneFast reconfigures the topology to account for the failure of link L1. Figure 11 BackboneFast Example After Indirect Link Failure Switch A (Root) Switch B L1 Link failure L2 L3 Switch C BackboneFast changes port through listening and learning states to forwarding state. 44964 If a new switch is introduced into a shared-medium topology as shown in Figure 12, BackboneFast is not activated because the inferior BPDUs did not come from the recognized designated bridge (Switch B). The new switch begins sending inferior BPDUs that say it is the root switch. However, the other switches ignore these inferior BPDUs, and the new switch learns that Switch B is the designated bridge to Switch A, the root switch. Figure 12 Adding a Switch in a Shared-Medium Topology Switch A (Root) Switch C Blocked port Switch B (Designated bridge) Added switch 44965 Cisco IOS Release 12.2(2)XT, 12.2(8)T, and 12.2(15)ZJ 23