Cisco NME-16ES-1G User Guide - Page 27
Handling Fragmented and Unfragmented Traffic, Using ACLs to Control Traffic to a Network - p config
 |
UPC - 882658036101
View all Cisco NME-16ES-1G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 27 highlights
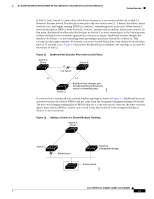
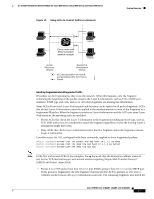
16- and 36-Port Ethernet Switch Module for Cisco 2600 Series, Cisco 3600 Series, and Cisco 3700 Series Figure 13 Using ACLs to Control Traffic to a Network Feature Overview Host A Cisco router with Ethernet switch network module Host B Human Resources network Research & Development network = ACL denying traffic from Host B and permitting traffic from Host A = Packet 88853 Handling Fragmented and Unfragmented Traffic IP packets can be fragmented as they cross the network. When this happens, only the fragment containing the beginning of the packet contains the Layer 4 information, such as TCP or UDP port numbers, ICMP type and code, and so on. All other fragments are missing this information. Some ACEs do not check Layer 4 information and therefore can be applied to all packet fragments. ACEs that do test Layer 4 information cannot be applied in the standard manner to most of the fragments in a fragmented IP packet. When the fragment contains no Layer 4 information and the ACE tests some Layer 4 information, the matching rules are modified: • Permit ACEs that check the Layer 3 information in the fragment (including protocol type, such as TCP, UDP, and so on) are considered to match the fragment regardless of what the missing Layer 4 information might have been. • Deny ACEs that check Layer 4 information never match a fragment unless the fragment contains Layer 4 information. Consider access list 102, configured with these commands, applied to three fragmented packets: Switch (config)# access-list 102 permit tcp any host 10.1.1.1 eq smtp Switch (config)# access-list 102 deny tcp any host 10.1.1.2 eq telnet Switch (config)# access-list 102 deny tcp any any Note In the first and second ACEs in the examples, the eq keyword after the destination address means to test for the TCP-destination-port well-known numbers equaling Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) and Telnet, respectively. • Packet A is a TCP packet from host 10.2.2.2, port 65000, going to host 10.1.1.1 on the SMTP port. If this packet is fragmented, the first fragment matches the first ACE (a permit), as if it were a complete packet because all Layer 4 information is present. The remaining fragments also match the Cisco IOS Release 12.2(2)XT, 12.2(8)T, and 12.2(15)ZJ 27