Cisco NME-16ES-1G User Guide - Page 22
Protocol Data Unit PDU called the Root Link Query PDU. The switch sends the Root Link Query PDU - p trunking
 |
UPC - 882658036101
View all Cisco NME-16ES-1G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 22 highlights
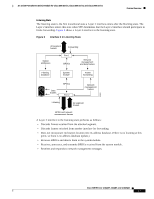
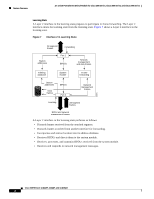
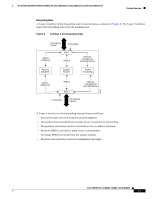
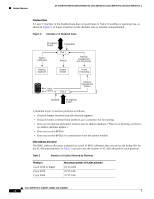
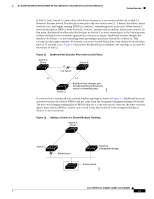
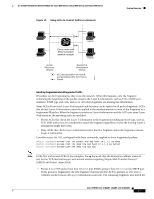
Feature Overview 16- and 36-Port Ethernet Switch Module for Cisco 2600 Series, Cisco 3600 Series, and Cisco 3700 Series cost values to interfaces that you want spanning tree to select last. If all interfaces have the same cost value, spanning tree puts the interface with the lowest interface number in the forwarding state and blocks other interfaces. The possible cost range is 0 to 65535 (the default is media-specific). Spanning tree uses the port cost value when the interface is configured as an access port and uses VLAN port cost values when the interface is configured as a trunk port. BackboneFast BackboneFast is initiated when a root port or blocked port on a switch receives inferior BPDUs from its designated bridge. An inferior BPDU identifies one switch as both the root bridge and the designated bridge. When a switch receives an inferior BPDU, it means that a link to which the switch is not directly connected (an indirect link) has failed (that is, the designated bridge has lost its connection to the root switch). Under STP rules, the switch ignores inferior BPDUs for the configured maximum aging time specified by the spanning-tree max-age global configuration command. The switch tries to determine if it has an alternate path to the root switch. If the inferior BPDU arrives on a blocked port, the root port and other blocked ports on the switch become alternate paths to the root switch. (Self-looped ports are not considered alternate paths to the root switch.) If the inferior BPDU arrives on the root port, all blocked ports become alternate paths to the root switch. If the inferior BPDU arrives on the root port and there are no blocked ports, the switch assumes that it has lost connectivity to the root switch, causes the maximum aging time on the root to expire, and becomes the root switch according to normal STP rules. If the switch has alternate paths to the root switch, it uses these alternate paths to transmit a new kind of Protocol Data Unit (PDU) called the Root Link Query PDU. The switch sends the Root Link Query PDU on all alternate paths to the root switch. If the switch determines that it still has an alternate path to the root, it causes the maximum aging time on the ports on which it received the inferior BPDU to expire. If all the alternate paths to the root switch indicate that the switch has lost connectivity to the root switch, the switch causes the maximum aging times on the ports on which it received an inferior BPDU to expire. If one or more alternate paths can still connect to the root switch, the switch makes all ports on which it received an inferior BPDU its designated ports and moves them out of the blocking state (if they were in the blocking state), through the listening and learning states, and into the forwarding state. Figure 10 shows an example topology with no link failures. Switch A, the root switch, connects directly to Switch B over link L1 and to Switch C over link L2. The interface on Switch C that connects directly to Switch B is in the blocking state. Figure 10 BackboneFast Example Before Indirect Link Failure Switch A (Root) Switch B L1 L2 L3 Blocked port Switch C 44963 Cisco IOS Release 12.2(2)XT, 12.2(8)T, and 12.2(15)ZJ 22