Cisco NME-16ES-1G User Guide - Page 47
Configuring Layer 2 Interfaces
 |
UPC - 882658036101
View all Cisco NME-16ES-1G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 47 highlights
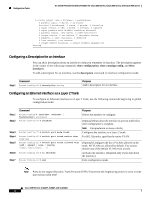
16- and 36-Port Ethernet Switch Module for Cisco 2600 Series, Cisco 3600 Series, and Cisco 3700 Series Configuration Tasks • Configuring Power Management on the Interface, page 98 • Configuring IP Multicast Layer 3 Switching, page 98 • Configuring IGMP Snooping, page 102 • Configuring Global Storm-Control, page 104 • Configuring Per-Port Storm-Control, page 106 • Configuring Separate Voice and Data Subnets, page 107 • Configuring Intrachassis Stacking, page 119 • Configuring Flow Control on Gigabit Ethernet Ports, page 119 • Configuring Layer 3 Interfaces, page 120 • Configuring Fallback Bridging, page 121 Configuring Layer 2 Interfaces • Configuring a Range of Interfaces (required) • Defining a Range Macro (optional) • Configuring Layer 2 Optional Interface Features (optional) • Configuring an Ethernet Interface as a Layer 2 Trunk (optional) • Configuring an Ethernet Interface as a Layer 2 Access (optional) Configuring a Range of Interfaces To configure a range of interfaces, use the interface range command in global configuration mode: Step 1 Command Purpose Router(config)# interface range {vlan vlan-id vlan-id} | {{ethernet | fastethernet | macro macro-name} slot/interface - interface}[, {{ethernet | fastethernet | macro macro-name} slot/interface - interface}] Selects the range of interfaces to be configured. • The space before the dash is required. For example, the command interface range fastethernet 1 - 5 is valid; the command interface range fastethernet 1-5 is not valid. • You can enter one macro or up to five comma-separated ranges. • Comma-separated ranges can include both VLANs and physical interfaces. • You are not required to enter spaces before or after the comma. • The interface range command only supports VLAN interfaces that are configured with the interface vlan command. Cisco IOS Release 12.2(2)XT, 12.2(8)T, and 12.2(15)ZJ 47