Cisco WS-C2960S-24PD-L Software Guide - Page 131
Using DHCP-Based Autoconfiguration
 |
View all Cisco WS-C2960S-24PD-L manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 131 highlights
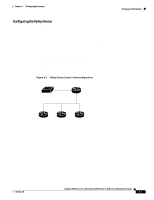
Chapter 6 Configuring the System Changing IP Information Use this procedure to remove the IP information from a switch. Note Using the no ip address command in configuration mode disables the IP protocol stack as well as removes the IP information. Cluster members without IP addresses rely on the IP protocol stack being enabled. Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps to remove an IP address: Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Command clear ip address vlan 1 ip_address subnet_mask end show running-config Purpose Remove the IP address and subnet mask. Return to privileged EXEC mode. Verify that the information was removed by displaying the running configuration. Using DHCP-Based Autoconfiguration The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) provides configuration information to Internet hosts and internetworking devices. With DHCP-based autoconfiguration, your switch (DHCP client) can be automatically configured during bootup with IP address information and a configuration file that it receives during DHCP-based autoconfiguration. Note DHCP replaces the Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) feature autoconfiguration to ensure retrieval of configuration files by unicast TFTP messages. BOOTP is available in earlier software releases for this switch. Understanding DHCP-Based Autoconfiguration The DHCP provides configuration information to internet hosts and internetworking devices. This protocol consists of two components: one for delivering configuration parameters from a DHCP server to a device and one for allocating network addresses to devices. DHCP is built on a client-server model, where designated DHCP servers allocate network addresses and deliver configuration parameters to dynamically configured devices. With DHCP-based autoconfiguration, your switch (DHCP client) can be automatically configured at startup with IP address information and a configuration file that it receives during DHCP-based autoconfiguration. No DHCP client-side configuration is required on your switch. However, you need to configure the DHCP server for various lease options. You might also need to configure a TFTP server, a Domain Name System (DNS) server, and possibly a relay device if the servers are on a different LAN than your switch. A relay device forwards broadcast traffic between two directly connected LANs. A router does not forward broadcast packets, but it forwards packets based on the destination IP address in the received packet. DHCP-based autoconfiguration replaces the BOOTP client functionality on your switch. 78-6511-08 Catalyst 2900 Series XL and Catalyst 3500 Series XL Software Configuration Guide 6-3